Antibacterial Soap May Be Destroying Your Gut Health

TL;DR: Your heartbeat pattern directly influences brain function, focus, and emotional control through measurable psychophysiological coherence. Simple breathing techniques can synchronize heart-brain communication to enhance cognitive performance and reduce stress within minutes.

Scientists have discovered something that seems almost impossible: your heartbeat can directly influence how well your brain functions. And it's not just about pumping blood. The pattern of your heartbeat - its rhythm, its variability - can measurably boost your focus, memory, and emotional control.
This phenomenon is called psychophysiological coherence, and it represents a fundamental shift in how we understand the relationship between body and mind. For decades, we assumed the brain was in charge, sending orders to the heart. Turns out, the conversation is much more interesting than that.
Here's what researchers at the HeartMath Institute discovered: the heart sends more signals to the brain than the brain sends to the heart. Much more. About 80-90% of the fibers in the vagus nerve - the main communication highway between your heart and brain - carry information upward, from heart to brain.
Think about that for a second. Your heart isn't just a pump waiting for commands. It's got its own nervous system with roughly 40,000 neurons, sophisticated enough to be called a "heart brain." And it's constantly sending information that shapes how your actual brain processes emotions, makes decisions, and focuses attention.
Your heart sends more information to your brain than your brain sends to your heart - about 80-90% of vagus nerve fibers carry signals upward, not downward.
The vagus nerve acts as the primary conduit for this conversation. According to Wikipedia's entry on the vagus nerve, this is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system, and the majority of its fibers are sensory. So when we talk about heart-brain communication, we're describing an anatomical reality, not a metaphor.
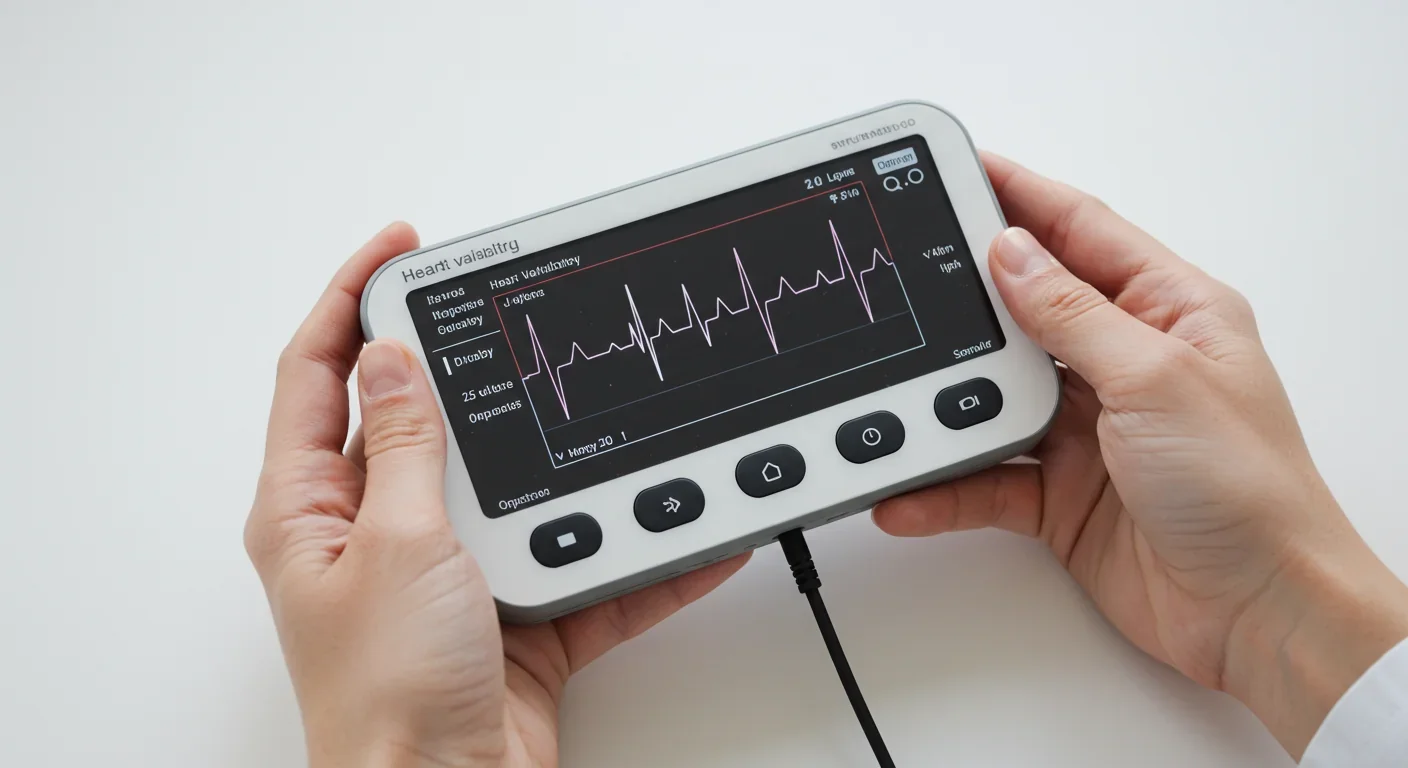
So what is coherence, exactly? It's not relaxation. It's not meditation. It's a specific, measurable state where your heart rhythm becomes smooth and ordered - like a sine wave at about 0.1 Hz.
When you're stressed or anxious, your heart rate variability (HRV) looks erratic and jagged on a graph. But when you achieve coherence, that pattern transforms into something elegant and rhythmic. And when your heart enters this state, something remarkable happens: your breathing automatically synchronizes with it, your blood pressure rhythms entrain, and your entire autonomic nervous system shifts into a coordinated dance.
This isn't just pretty data. Research from the HeartMath Institute involving over 11,500 participants who practiced coherence techniques for 6-9 weeks documented dramatic improvements:
• 24% improvement in focus
• 30% improvement in sleep quality
• 56% reduction in depression
• 46% reduction in anxiety
• 48% reduction in fatigue
Those aren't marginal gains. Those are life-changing numbers.
The mechanism linking heart rhythms to brain function centers on what neuroscientists call the neurocardiac axis. When your heart rate variability increases in this coherent pattern, it signals the brain that everything's under control. This activates the parasympathetic nervous system - your rest-and-digest mode - while calming the sympathetic fight-or-flight response.
Recent research from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus revealed something even more specific: vagus nerve stimulation connects directly to the cholinergic system that regulates attention and learning. When researchers stimulated the vagus nerve in healthy mice during a learning task, the animals learned faster and reached higher performance levels.
"We concluded that there is a direct connection between the vagus nerve, the cholinergic system that regulates certain aspects of brain function, and motor cortex neurons that are essential in learning new skills."
- Dr. Cristin Welle, University of Colorado
A 2024 PubMed study involving 143 healthy young adults found that participants with higher resting vagal tone - measured through heart rate variability - showed superior performance on tasks requiring cognitive control, inhibition, cognitive flexibility, and working memory compared to those with lower vagal tone.
The researchers noted that vagally mediated heart rate variability is now considered "an index of top-down control processes involved in cognition and emotion regulation." In other words, a coherent heart rhythm isn't just correlated with better thinking - it actively supports the brain's executive functions.
The beauty of coherence is that you don't need expensive equipment or years of training to experience it. The most basic technique involves controlled breathing and positive emotion, which you can do right now.
According to research summarized by HeartMath, here's the foundational practice:
The Quick Coherence Technique:
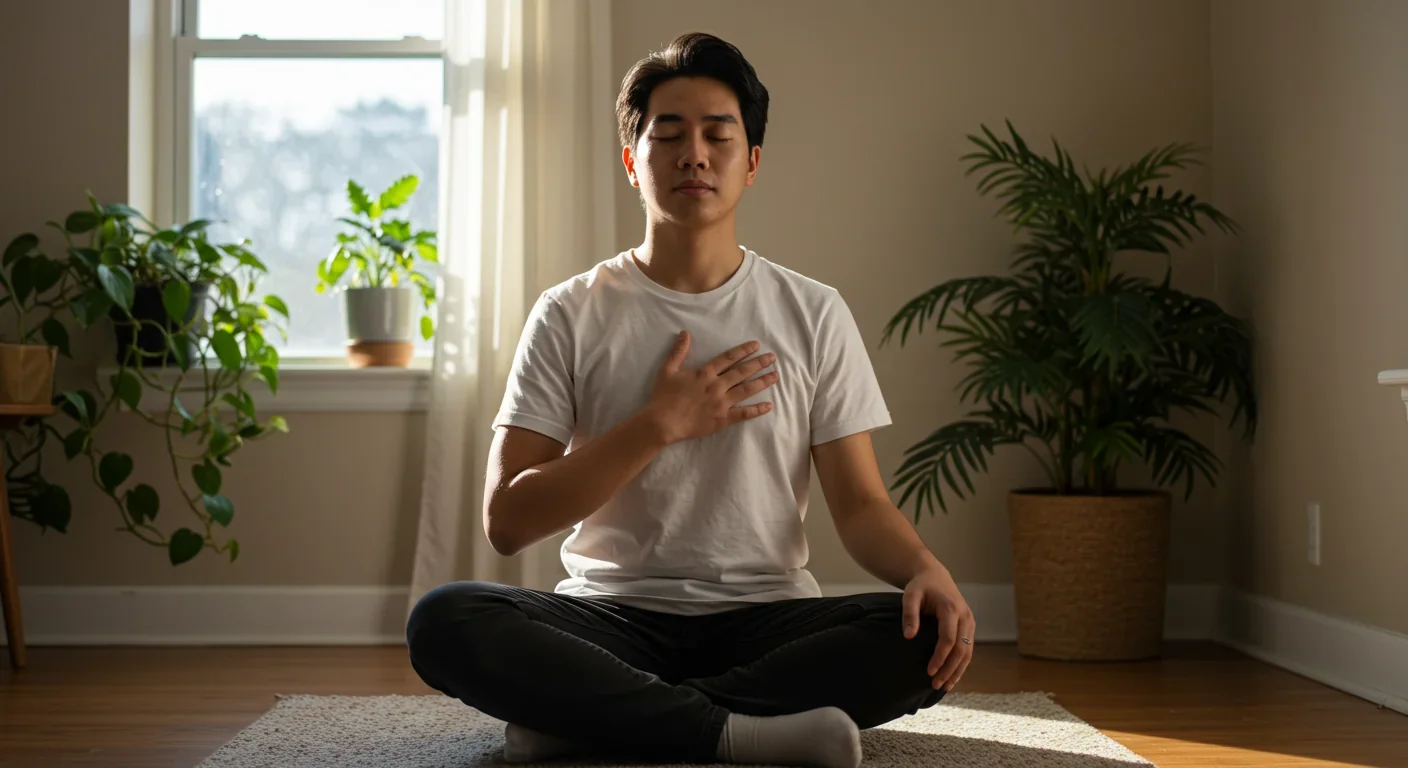
1. Heart Focus: Place your attention on the area around your heart. You can put your hand over your heart to help direct focus.
2. Heart Breathing: Breathe slowly and deeply, imagining your breath flowing in and out through your heart area. Aim for about 5 seconds on the inhale, 5 seconds on the exhale. This 10-second rhythm naturally produces a coherent heart pattern at the optimal 0.1 Hz frequency.
3. Heart Feeling: As you continue this breathing pattern, activate a positive emotion. Recall a specific time when you felt genuine appreciation, care, or compassion. Don't just think about it - try to feel it in your chest area.
That's it. Simple but not always easy, especially when you're stressed. The key is that breathing alone can induce coherence, but adding the positive emotion amplifies and stabilizes the effect.
Research shows that even beginners can achieve measurable coherence states within minutes of practice. The HeartMath Institute reports that when people use this technique during a 10-minute session, their heart, blood pressure, and respiration rhythms all entrain - oscillating at the same frequency.

While you can practice coherence without any tools, biofeedback devices make the invisible visible. Products like the HeartMath Inner Balance sensor or EmWave measure your HRV in real-time and show you when you're in coherence.
This instant feedback transforms an abstract physiological state into a trainable skill. You see the jagged, erratic pattern of stress smoothing into the ordered waves of coherence. Over time, you learn what coherence feels like, and you can access it without the device.
Research published in Frontiers in Psychology found that athletes who used HRV-guided training showed improvements in performance metrics. The study on elite downhill mountain bikers found that hypnosis combined with HRV monitoring helped athletes reduce anxiety, improve self-confidence, and enhance both performance and HRV measures.
For anyone interested in quantified self-improvement, HRV biofeedback offers something rare: a scientifically validated metric that you can influence directly through mental and breathing techniques.
The applications of coherence training have expanded far beyond stress management. Here's where the research is showing real-world impact:
Education: Schools implementing HeartMath programs have reported improvements in student focus, test performance, and behavioral issues. When kids learn to regulate their heart rhythms before tests or challenging situations, they access better executive function.
Athletics: Professional athletes and teams use HRV training to optimize performance and recovery. A recent study on psychophysiological states in exercise demonstrated how identifying functional and dysfunctional zones through HRV, skin conductance, and respiratory rates can optimize athletic performance. Machine learning models are now being used to predict athlete readiness based on these psychophysiological markers.
Workplace Performance: Companies training employees in coherence techniques report reductions in workplace stress and improvements in decision-making and teamwork. When your autonomic nervous system isn't in constant fight-or-flight, you think more clearly and collaborate more effectively.
After 6-9 weeks of coherence practice, participants experienced a 56% reduction in depression, 46% reduction in anxiety, and 24% improvement in focus.
Clinical Settings: Emerging research suggests vagus nerve stimulation and HRV training may help patients recovering from stroke, traumatic brain injury, PTSD, and other neurological conditions. Dr. Welle from the University of Colorado study noted: "I think there's a huge untapped potential for using vagus nerve stimulation to help the brain heal itself."
The neurocardiology research shows that chronic stress creates elevated sympathetic tone and reduced heart rate variability, which increases risk of arrhythmias and potentially disrupts cognitive function. Coherence training essentially reverses this pattern.

Coherence isn't the only game in town for cognitive enhancement. Meditation, mindfulness, physical exercise, and even pharmacological interventions all claim cognitive benefits. So how does coherence stack up?
Unlike meditation, which often takes years to master and produces varied results, coherence can be achieved in minutes and measured objectively. A study on mindfulness in football penalty shootouts found that mindfulness training improved attentional control during high-pressure moments, but this required sustained practice over weeks.
Compared to stimulants like caffeine or prescription medications, coherence training has no side effects and becomes more effective with practice rather than building tolerance. And unlike passive interventions, coherence gives you an active skill you can deploy in real-time when you need it most.
The psychophysiology research positions HRV as an objective link between autonomic nervous system activity and cognitive-emotional states, making it a more measurable approach than subjective meditation practices.
What makes coherence particularly compelling is its accessibility. You don't need a gym membership, prescription, or extensive training. You need awareness of your heart, control of your breath, and the ability to recall a positive feeling.
Here's a detail that sounds like science fiction but checks out: your heart generates an electromagnetic field that extends several feet outside your body. According to research cited by HeartMath, the heart's electromagnetic field is about 60 times greater in amplitude than the brain's.
This field isn't just physically measurable - it changes based on your emotional state. When you're in coherence, that field becomes more organized and can actually be detected by people nearby. Some researchers hypothesize this might be one mechanism underlying our ability to "sense" someone else's emotional state, though this remains an area of active investigation.
The implications are fascinating. If your heart's electromagnetic field influences your own brain function and potentially affects people around you, then coherence isn't just personal optimization - it's social technology.
Despite the promising research, coherence science has limitations worth noting. Most of the extensive research on coherence techniques comes from the HeartMath Institute, which also sells the training products. While they cite over 300 peer-reviewed studies utilizing their techniques, independent replication across diverse research institutions would strengthen the evidence base.
The mechanisms are also not fully mapped. We know the vagus nerve connects heart and brain, we can measure HRV changes, and we see correlations with cognitive performance. But the complete picture of how exactly heart rhythms modulate specific brain regions and cognitive processes remains incomplete.
There's also individual variation. Some people achieve coherence easily; others struggle even with biofeedback. Factors like existing cardiovascular conditions, chronic stress, trauma history, and even genetic variations in autonomic nervous system function may influence responsiveness to training.
And while short-term benefits appear robust, more long-term studies tracking coherence practice over years would help establish whether benefits plateau, continue growing, or require ongoing maintenance.

If you want to explore coherence, here's a realistic approach based on the research:
Start Simple: Begin with 5 minutes of heart-focused breathing daily. Don't worry about perfect technique - just breath slowly through your heart area while recalling something that makes you genuinely grateful.
Track Your Progress: If you want objective feedback, invest in an HRV monitor. Even basic fitness trackers now include HRV measurements. Look for increases in your HRV readings over time, particularly your morning resting HRV.
Deploy Tactically: Use the quick coherence technique before high-stakes situations - presentations, difficult conversations, important decisions. The research suggests that even a few minutes can shift your autonomic state.
Be Consistent: The most significant benefits in the HeartMath studies came from 6-9 weeks of regular practice. Like any skill, coherence strengthens with repetition.
Combine Approaches: Coherence training works well alongside other practices. Athletes might pair it with physical training. Students might use it before studying or tests. Professionals might integrate it into their morning routine.
The 2024 cognitive functioning study provides new insights into body-brain interactions, further supporting that training your heart rhythm can meaningfully impact your cognitive abilities.
We're living through a fascinating moment in the science of human performance. For centuries, we assumed cognition was primarily a brain phenomenon. Now we're discovering that the body - particularly the heart - plays a more active role than we imagined.
This research suggests that peak performance isn't just about training your brain harder. It's about optimizing the conversation between your heart and brain. It's about recognizing that your nervous system is an integrated network, not a top-down hierarchy.
"I think there's a huge untapped potential for using vagus nerve stimulation to help the brain heal itself."
- Dr. Cristin Welle, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The practical implications are profound. Instead of seeing stress as something that happens to us, coherence training offers a way to actively shift our physiological state. Instead of accepting that our focus and emotional regulation are fixed traits, we can train them through the heart-brain connection.
For the millions of people dealing with anxiety, stress, or cognitive demands, coherence represents an evidence-based tool that's both simple and scientifically grounded. You don't need to change your entire life or invest in expensive interventions. You need to learn a breathing pattern and practice feeling positive emotions.
The University of Colorado research on vagus nerve stimulation and learning hints at even more possibilities. If we can enhance learning and recovery through heart-brain synchronization, we might be looking at a new frontier in education, rehabilitation, and human optimization.
Your heartbeat isn't just a vital sign - it's a signal. And that signal can be optimized to enhance how your brain functions, how you regulate emotions, and how effectively you perform under pressure.
Psychophysiological coherence gives us a measurable, trainable pathway to better cognitive performance and emotional stability. It's backed by decades of research, accessible to anyone, and produces results that can be tracked objectively.
The heart-brain connection represents one of the most democratizing discoveries in performance science. Elite athletes use it. So can you. The hardware - your heart, your vagus nerve, your autonomic nervous system - came standard with your body. Now we're just learning how to use it more effectively.
In a world that constantly demands more of our attention, focus, and resilience, understanding how to synchronize your heart and brain isn't just interesting science. It's practical wisdom backed by rigorous research. And it starts with something as simple as placing your attention on your heart and taking a slow, deep breath.
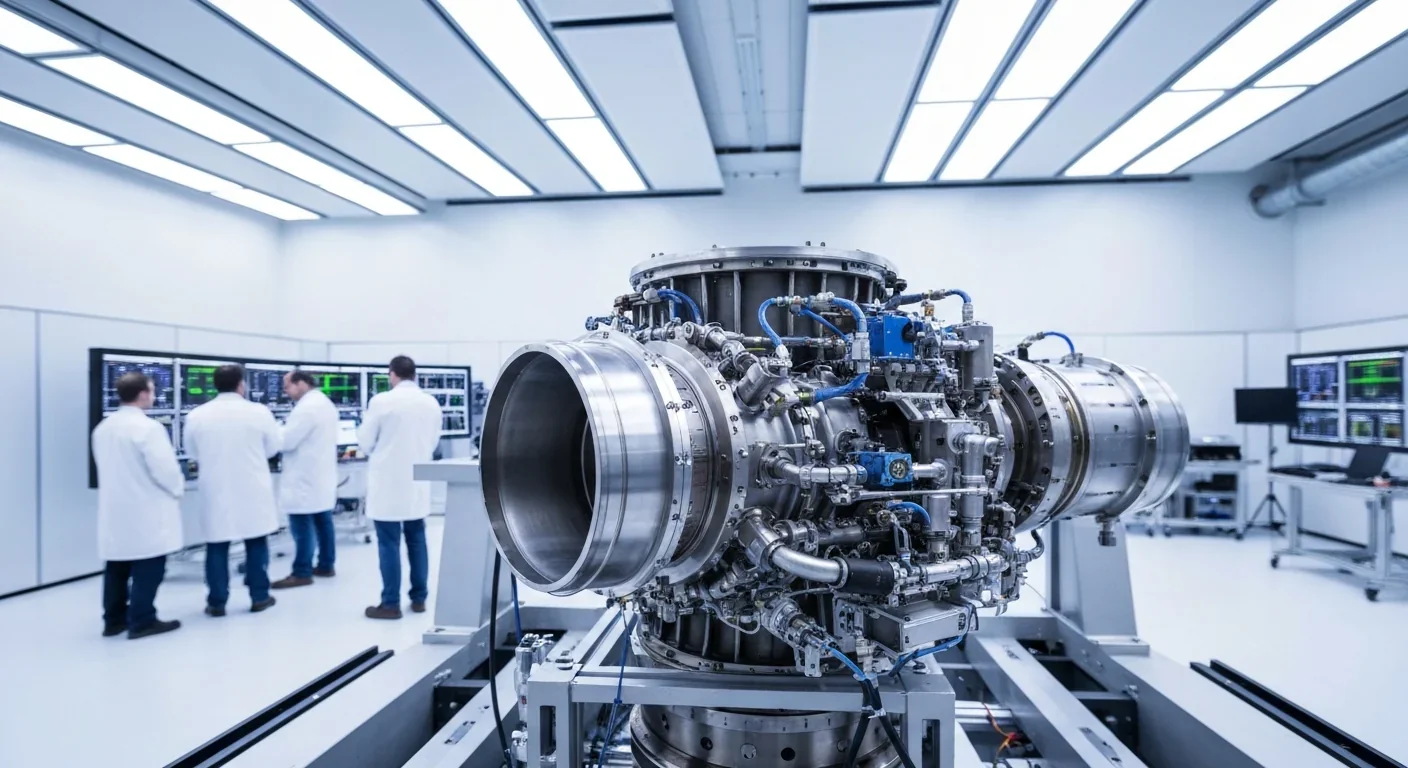

Rotating detonation engines use continuous supersonic explosions to achieve 25% better fuel efficiency than conventional rockets. NASA, the Air Force, and private companies are now testing this breakthrough technology in flight, promising to dramatically reduce space launch costs and enable more ambitious missions.

Triclosan, found in many antibacterial products, is reactivated by gut bacteria and triggers inflammation, contributes to antibiotic resistance, and disrupts hormonal systems - but plain soap and water work just as effectively without the harm.
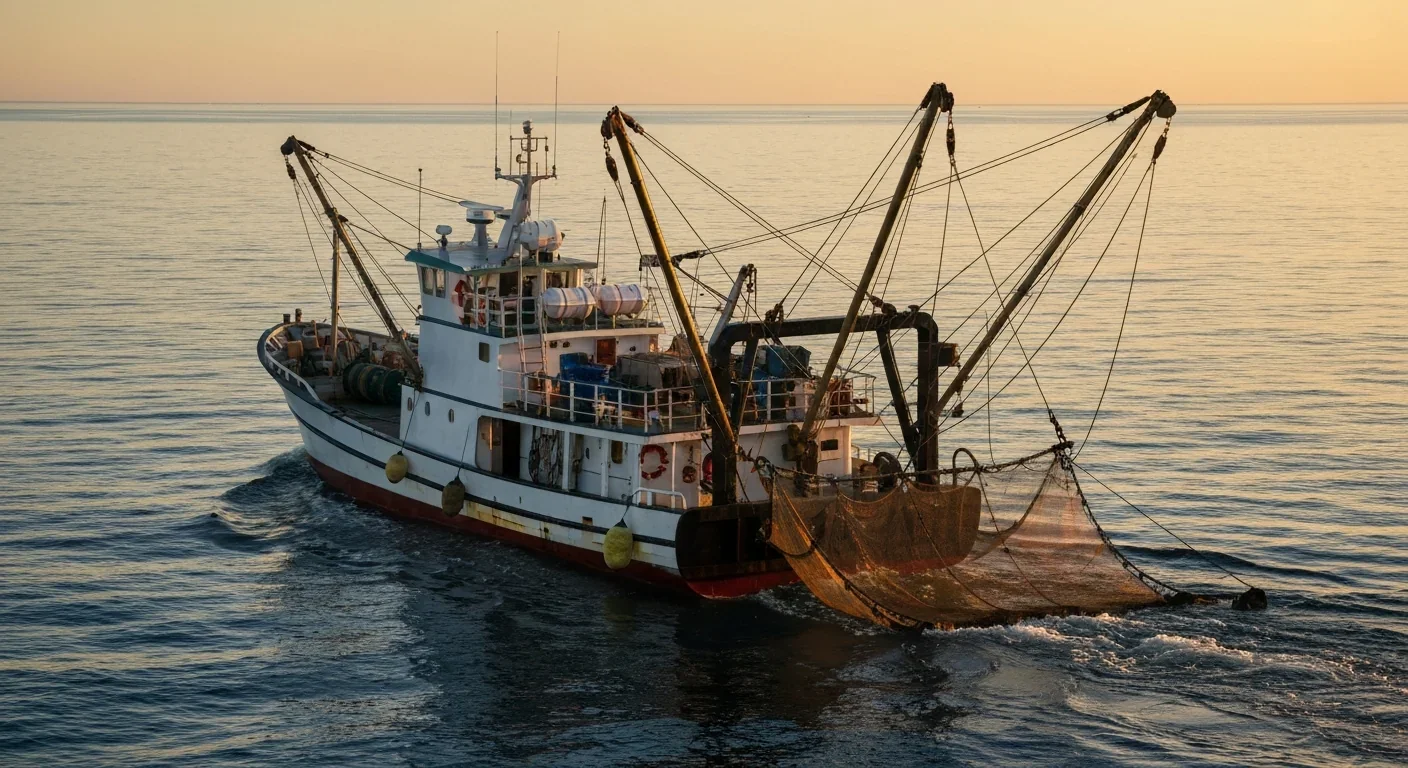

AI-powered cameras and LED systems are revolutionizing sea turtle conservation by enabling fishing nets to detect and release endangered species in real-time, achieving up to 90% bycatch reduction while maintaining profitable shrimp operations through technology that balances environmental protection with economic viability.
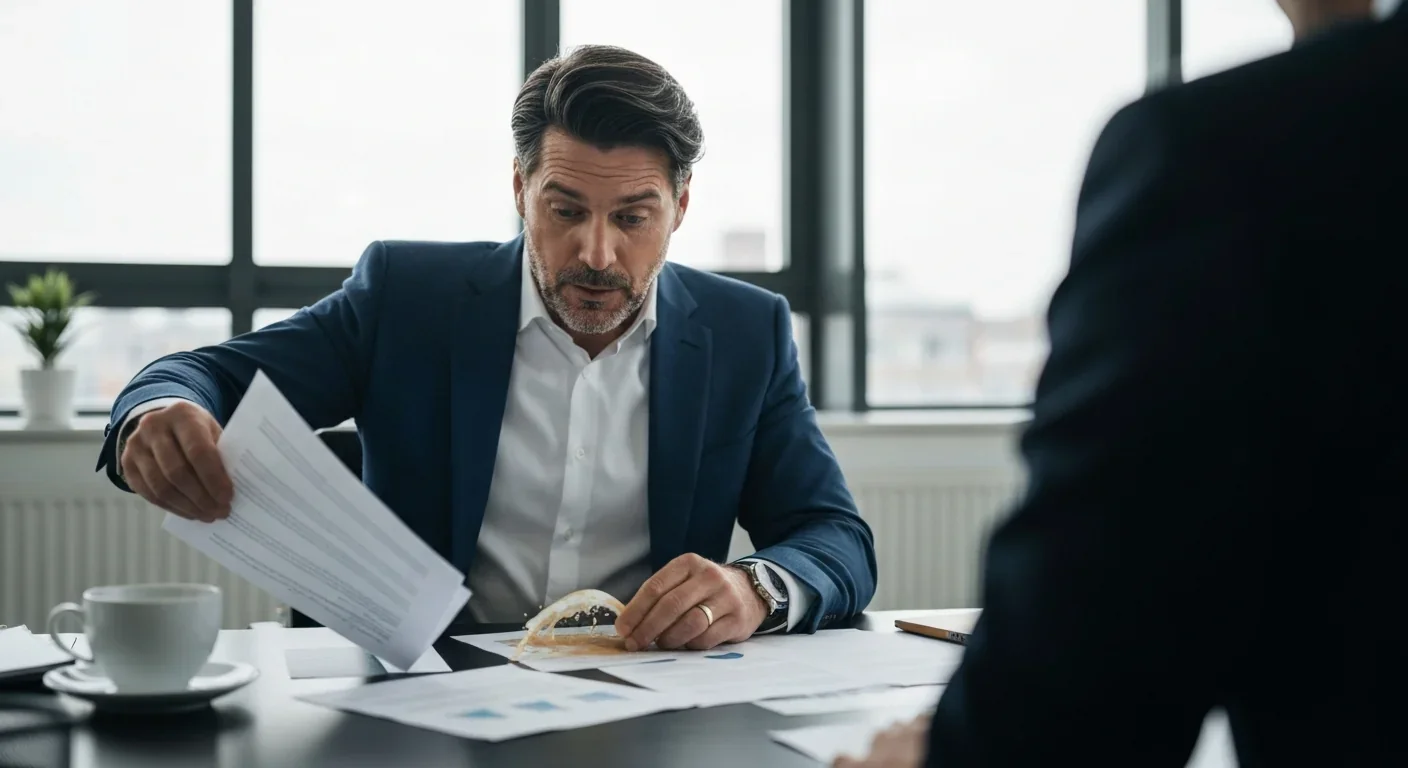

The pratfall effect shows that highly competent people become more likable after making small mistakes, but only if they've already proven their capability. Understanding when vulnerability helps versus hurts can transform how we connect with others.
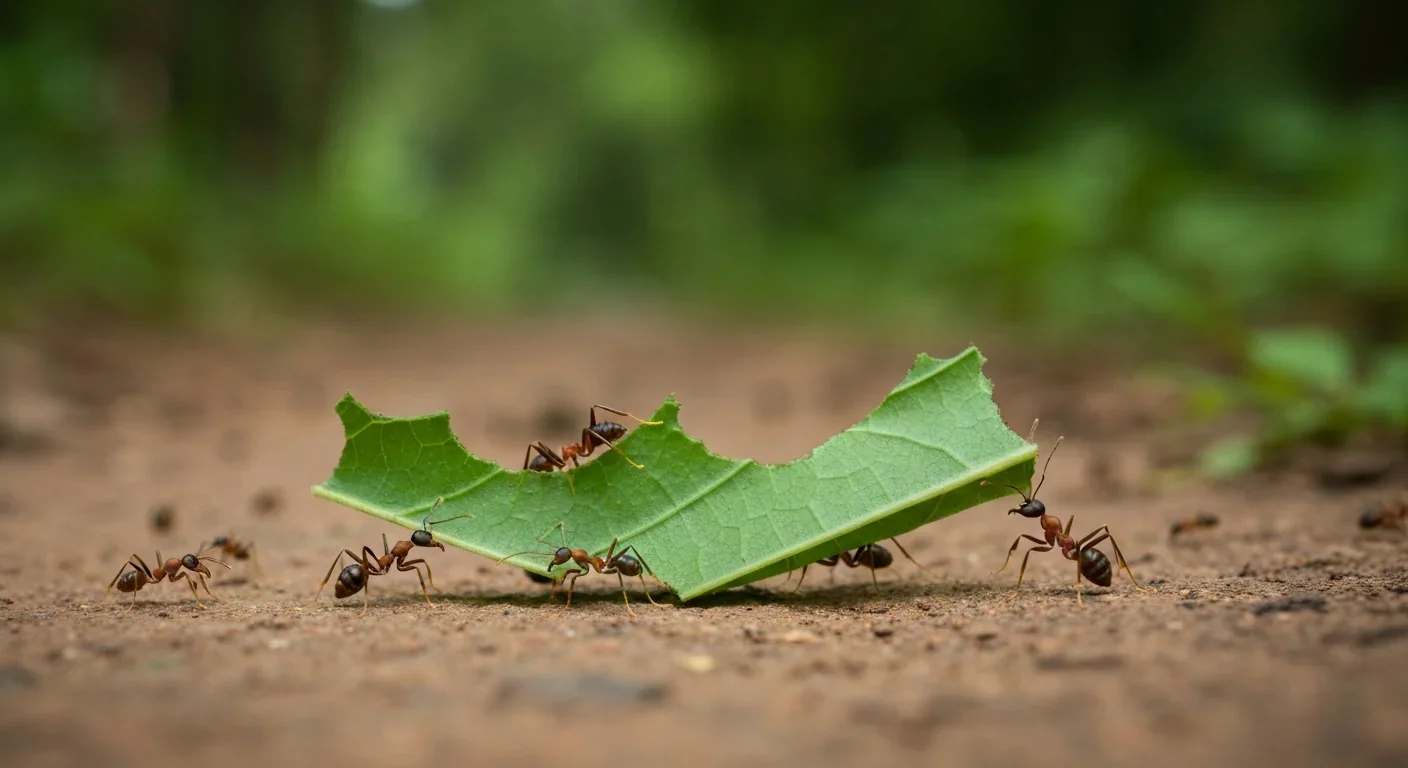

Leafcutter ants have practiced sustainable agriculture for 50 million years, cultivating fungus crops through specialized worker castes, sophisticated waste management, and mutualistic relationships that offer lessons for human farming systems facing climate challenges.

Gig economy platforms systematically manipulate wage calculations through algorithmic time rounding, silently transferring billions from workers to corporations. While outdated labor laws permit this, European regulations and worker-led audits offer hope for transparency and fair compensation.
Quantum computers face a critical but overlooked challenge: classical control electronics must operate at 4 Kelvin to manage qubits effectively. This requirement creates engineering problems as complex as the quantum processors themselves, driving innovations in cryogenic semiconductor technology.