The Ancient Protein Clock That Ticks Without DNA
Scientists discovered 24-hour protein rhythms in cells without DNA, revealing an ancient timekeeping mechanism that predates gene-based clocks by billions of years and exists across all life.

Scientists discovered 24-hour protein rhythms in cells without DNA, revealing an ancient timekeeping mechanism that predates gene-based clocks by billions of years and exists across all life.

Baroreceptors are specialized pressure sensors in your arteries that do far more than monitor blood pressure - they influence stress responses, emotional states, and mental health. New research reveals how these tiny sensors connect cardiovascular function to anxiety and depression, opening revolutionary treatment pathways from implanted devices to simple breathing techniques.

Segmented filamentous bacteria (SFB) colonize infant guts during weaning and train T-helper 17 immune cells, shaping lifelong disease resistance. Diet, antibiotics, and birth method affect this critical colonization window.
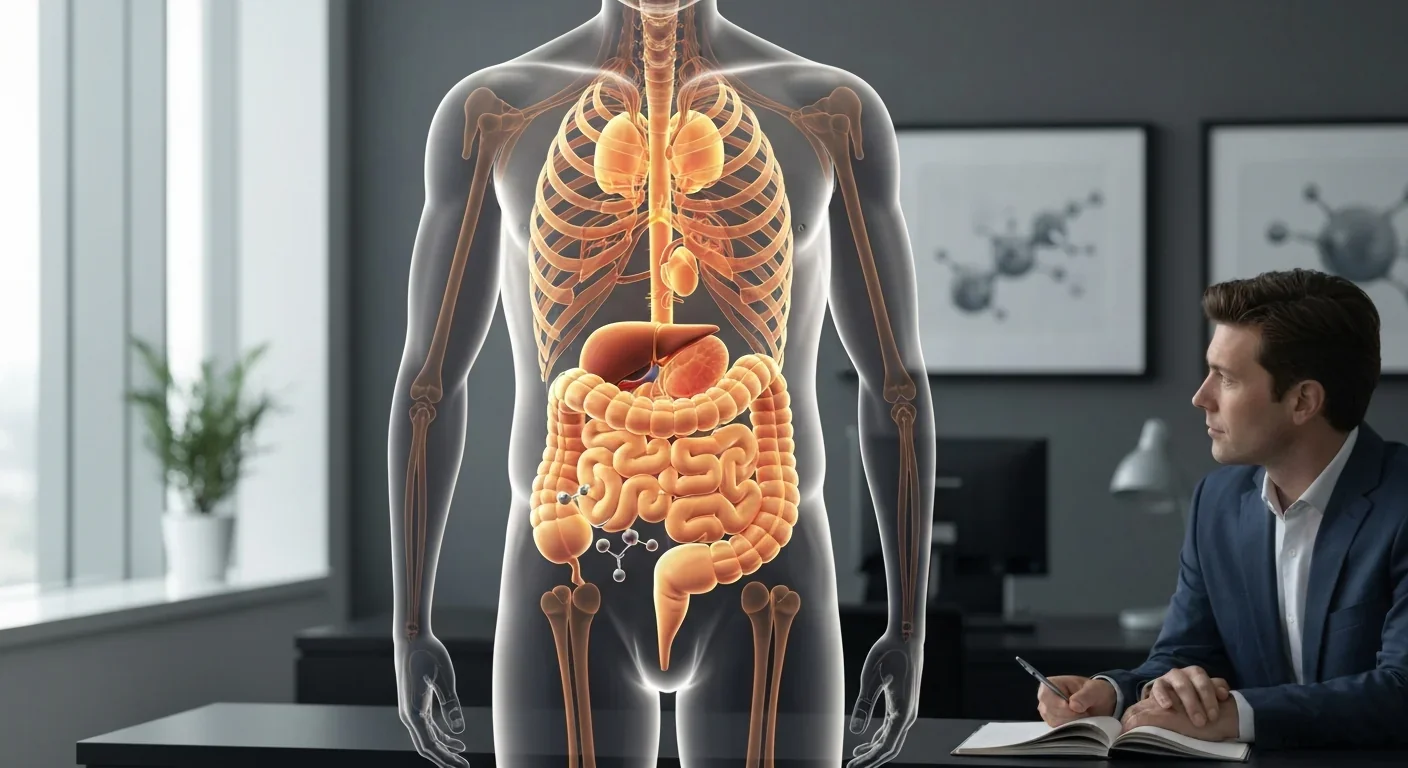
Gut bacteria transform bile acids into hormone-like molecules that regulate metabolism, immunity, and disease risk. Understanding this hidden endocrine system opens new therapeutic pathways for treating diabetes, obesity, and inflammation.
Ancient viral DNA sequences making up 45% of your genome are reactivating as you age, triggering brain inflammation that may drive Alzheimer's disease - but repurposed antiviral drugs show early promise in blocking this process.
Cells monitor ribosome production through a surveillance system that can either kill damaged cells or inadvertently create cancer. Understanding this molecular checkpoint is revealing new cancer therapies and explaining rare genetic disorders.
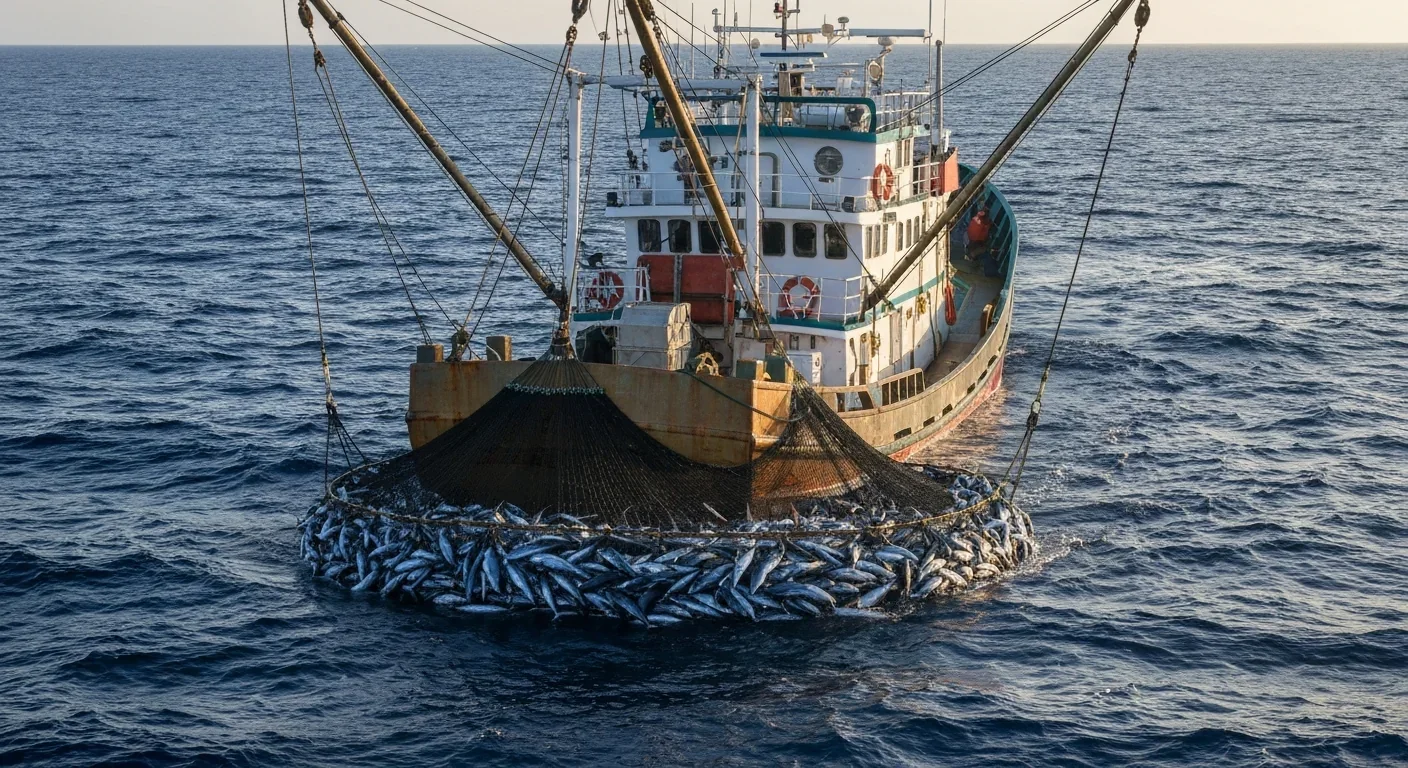

Banned pesticides like DDT persist in food chains for decades, concentrating in fatty fish and dairy products, then accumulating in human tissues where they disrupt hormones and increase health risks.

Nitrites in processed meats convert to N-nitroso compounds in your gut, directly damaging DNA and increasing cancer risk. Learn the biochemical mechanisms, which meats pose the highest risk, and evidence-based strategies to protect yourself.

Triclosan, found in many antibacterial products, is reactivated by gut bacteria and triggers inflammation, contributes to antibiotic resistance, and disrupts hormonal systems - but plain soap and water work just as effectively without the harm.

PET plastic bottles continuously leach hormone-disrupting chemicals like phthalates and antimony into beverages. These compounds interfere with human endocrine systems, particularly affecting pregnant people, children, and those trying to conceive. Practical alternatives like glass and stainless steel eliminate this exposure.

Nearly 3 million farmworkers suffer organophosphate pesticide poisoning annually, causing irreversible brain damage through acetylcholinesterase inhibition. Despite overwhelming evidence of neurotoxicity and safer alternatives, regulatory failures and industry lobbying allow continued use, creating a hidden epidemic of neurological harm.
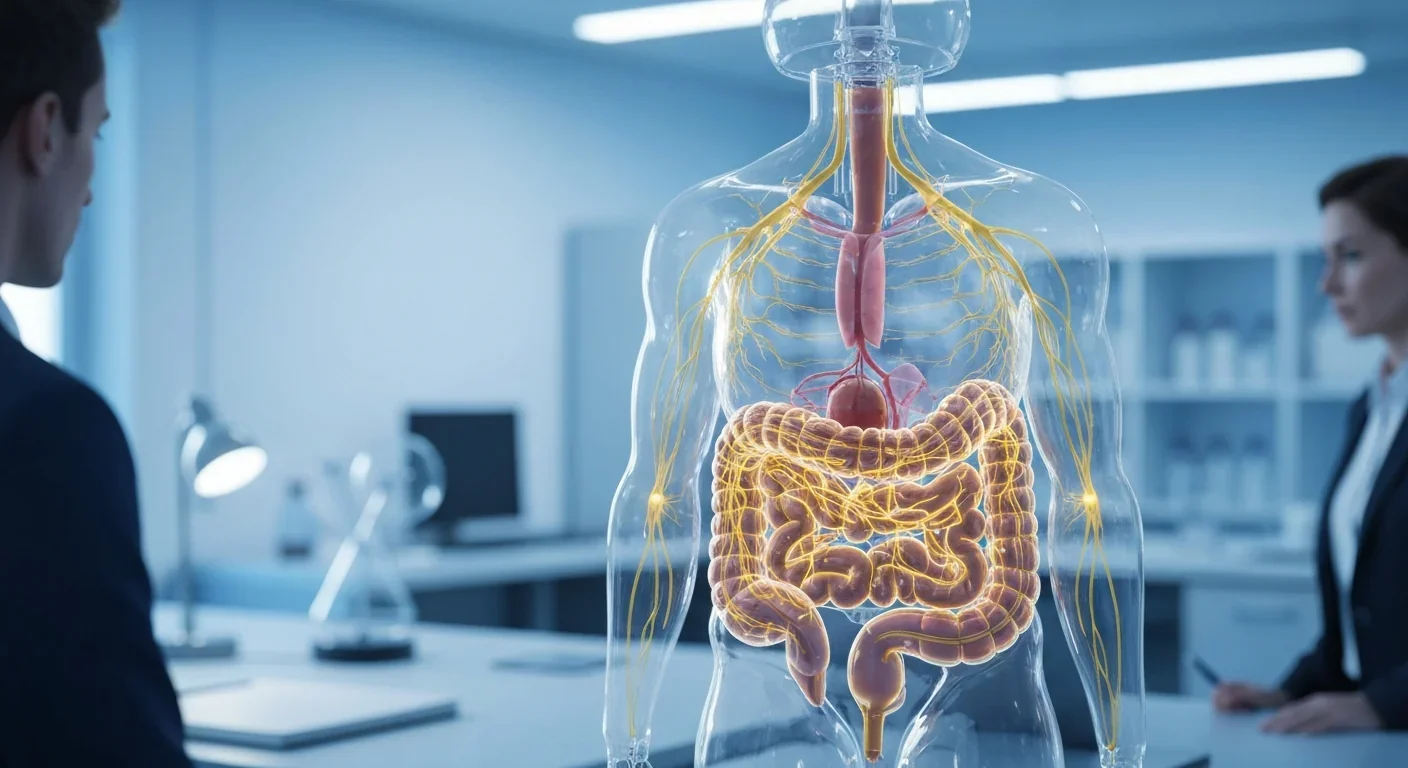
Your gut contains 500 million neurons that form a sophisticated second brain, producing 90% of your body's serotonin and constantly communicating with your brain through the vagus nerve. This gut-brain connection directly influences mood, anxiety, and mental health through neurotransmitter production and microbiome interactions.
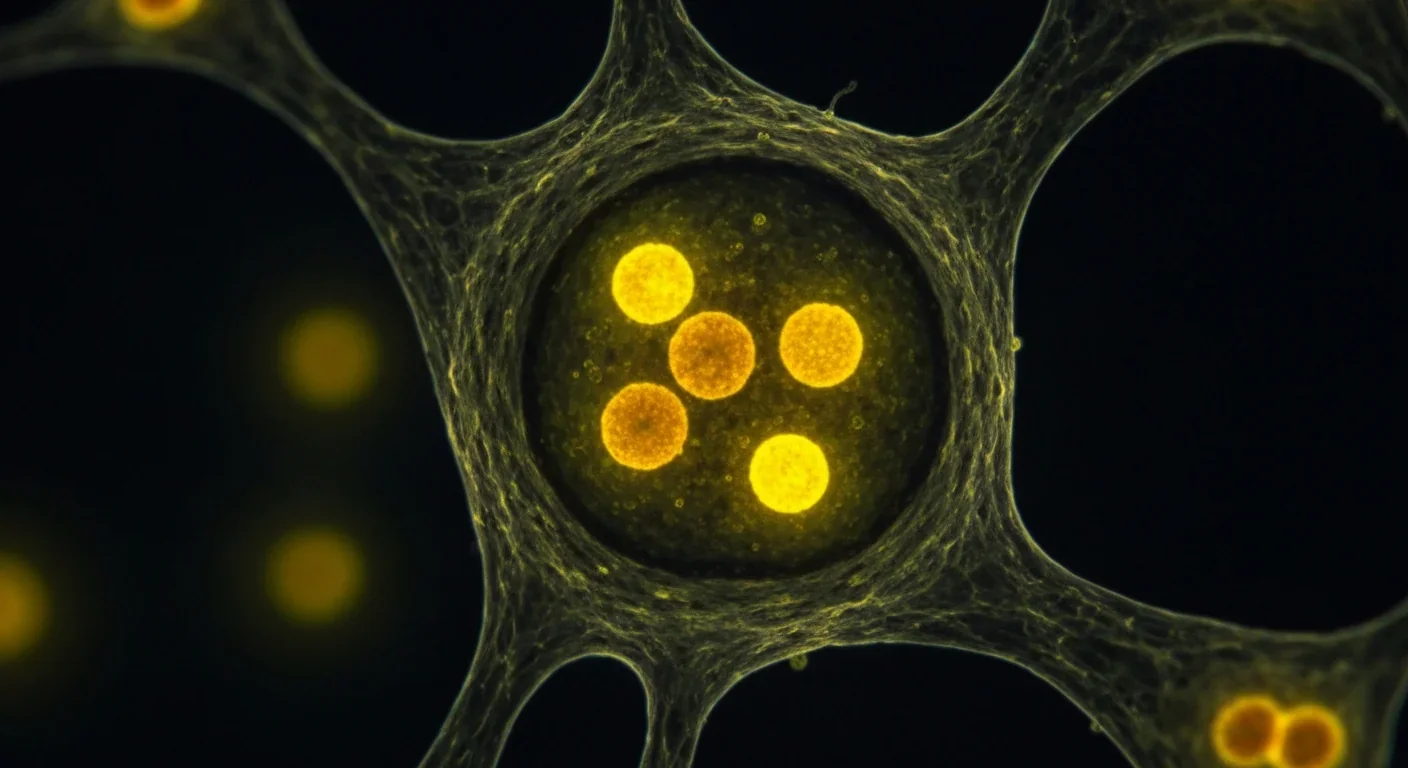
Lipofuscin, the 'age pigment' accumulating in cells, may predict biological aging more accurately than chronological age. This golden-brown cellular waste forms when lysosomes can't break down damaged proteins and fats, with rates varying dramatically between individuals based on genetics and lifestyle. Scientists are developing measurement techniques and therapeutic strategies to track and reduce lipofuscin, potentially revolutionizing how we assess health and develop anti-aging interventions.
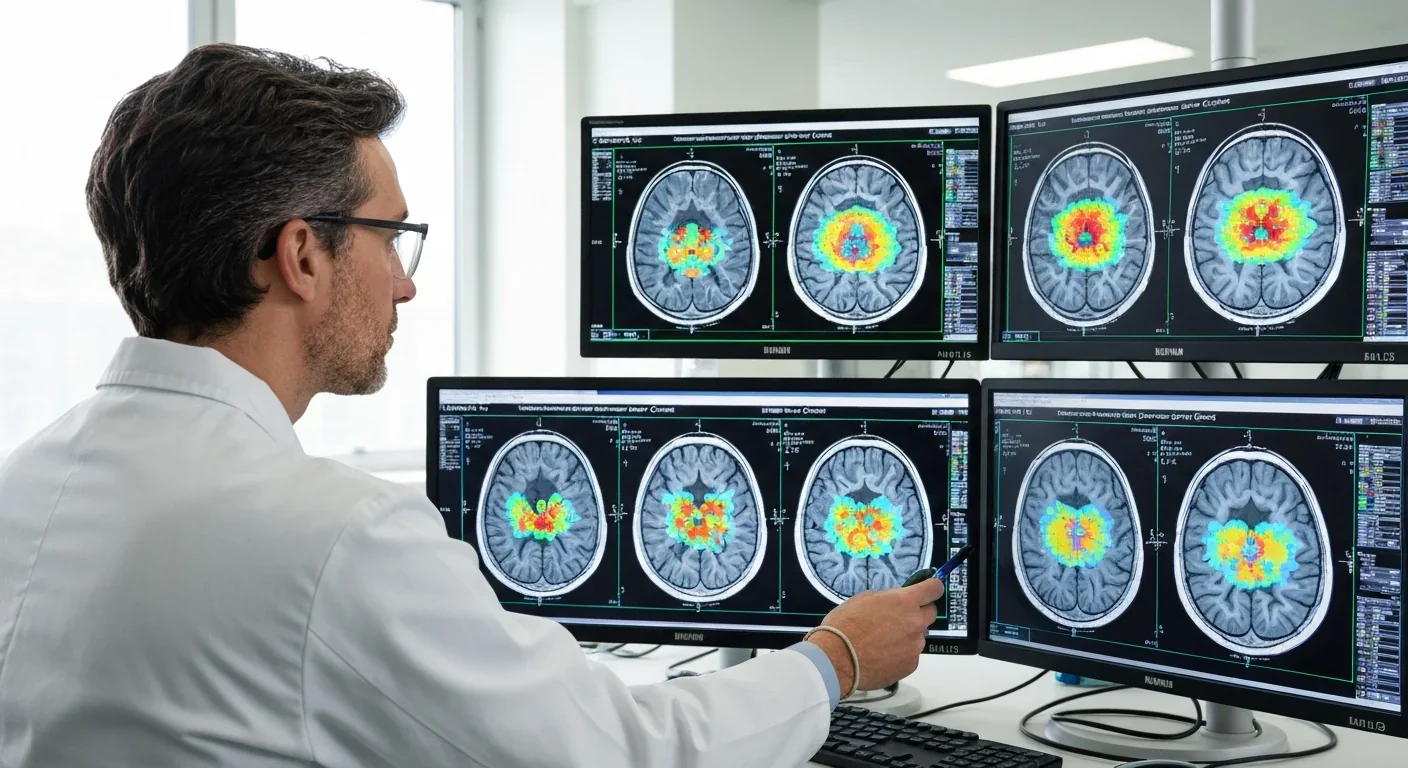
A groundbreaking 2025 study reveals the brain's map of the body remains surprisingly stable even years after amputation, overturning assumptions about phantom limb pain and forcing clinicians to rethink treatment approaches.

Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) has evolved from experimental therapy to FDA-approved medicine, achieving 85-94% cure rates for recurrent C. difficile infections where antibiotics fail. The treatment transplants healthy gut bacteria from screened donors via colonoscopy, capsules, or enema, restoring microbial balance through competitive exclusion.

CAR-T therapy genetically reprograms patients' immune cells to hunt cancer with remarkable success in blood cancers, achieving 50% remission in lymphoma and 80-90% in leukemia, though challenges remain with costs exceeding $1 million and limited effectiveness against solid tumors.
Deliberately cooling cardiac arrest patients to 32-34°C slows brain metabolism and prevents neurological damage, improving survival with good outcomes from 39% to 55%. This counter-intuitive intervention has evolved from strict protocols to flexible targeted temperature management.

Every night during deep sleep, your brain's glymphatic system clears toxic proteins linked to Alzheimer's. This waste clearance process depends on sleep quality, sleep stage, and even body position - making consistent, high-quality sleep essential for long-term brain health.
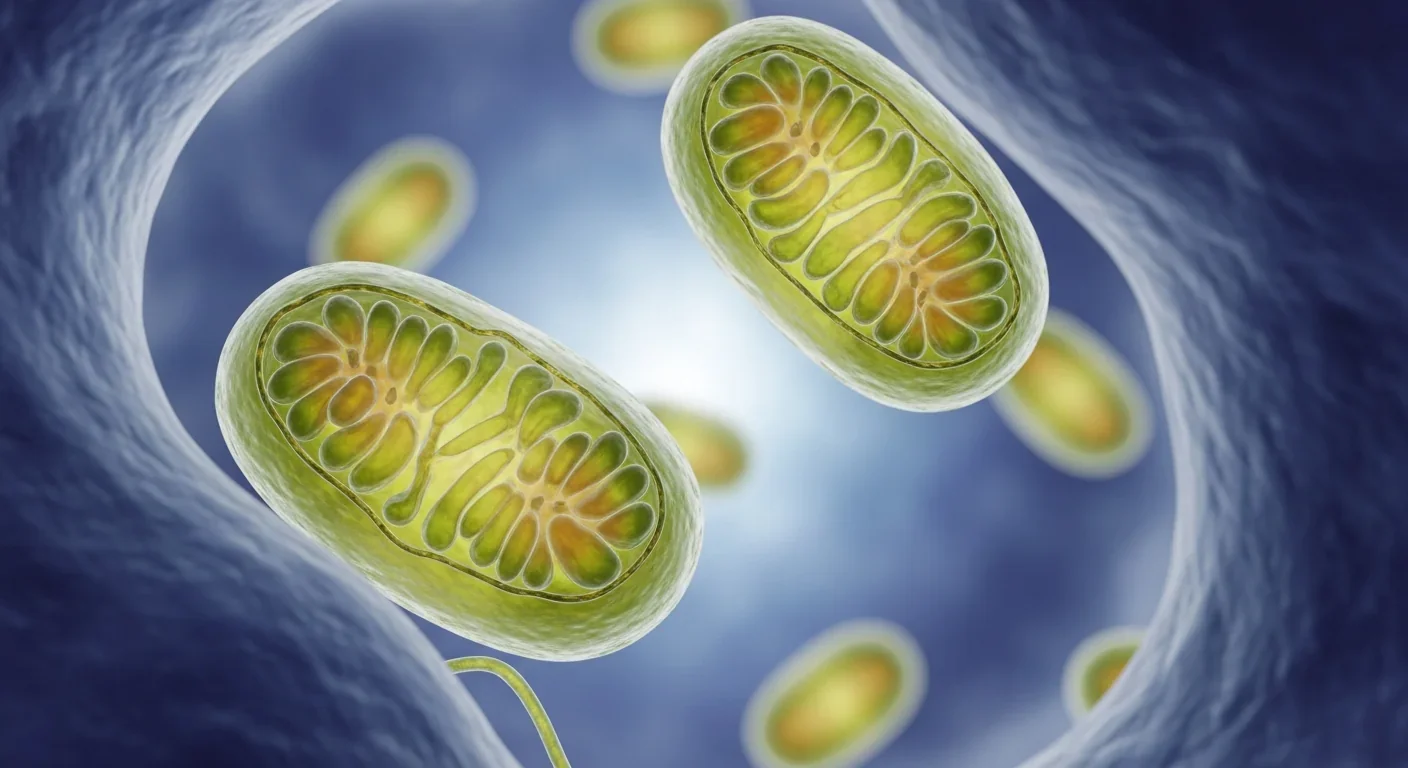
Scientists have discovered that controlled cellular stress in mitochondria activates protective responses that extend lifespan in model organisms. This mitochondrial unfolded protein response may explain why exercise, fasting, and other longevity interventions work at the molecular level.

Trees release airborne compounds called phytoncides that measurably reduce stress hormones, inflammation, and boost immune function. Just 15 minutes in the forest triggers biochemical changes that last for days.

The polyvagal ladder framework maps three nervous system states - social engagement, mobilization, and shutdown - revolutionizing trauma treatment by showing why trauma survivors can't simply "calm down" and providing state-specific regulation tools.

Scientists are using cutting-edge genomic techniques to decode the 70-80% of gut bacteria that can't be grown in labs, revealing their crucial roles in health and opening doors to personalized medicine.

Lysosomal storage diseases occur when genetic mutations disable the cellular recycling system, causing toxic waste to accumulate and damage organs. Gene therapy trials show unprecedented promise, with some patients discontinuing enzyme replacement therapy for months while maintaining health - offering hope for conditions once considered untreatable.

Between 30-50% of new buildings cause sick building syndrome through VOC off-gassing from common construction materials. This investigation reveals which products are the worst offenders, how to detect VOCs, and practical solutions including low-VOC alternatives now available at mainstream retailers.
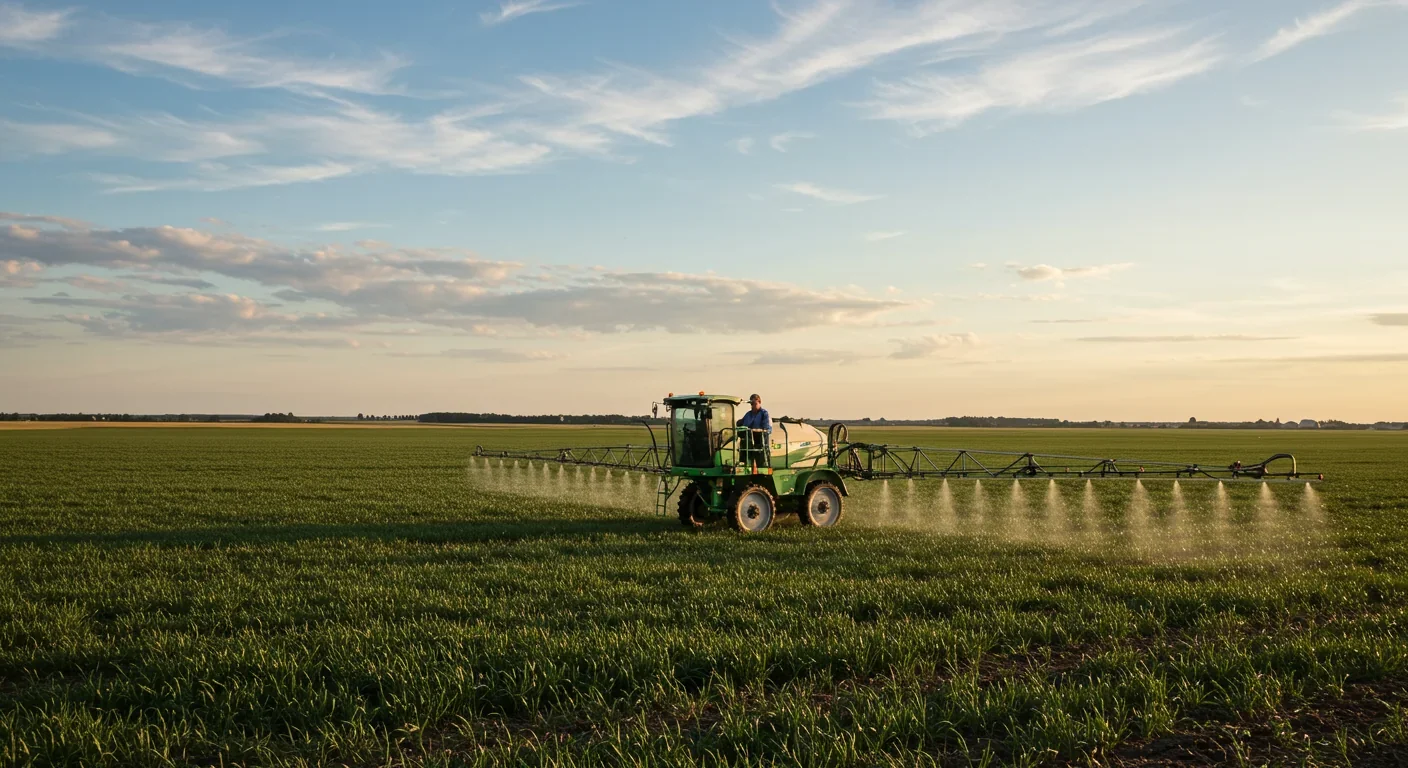

Agricultural pesticides drift miles from application sites through wind and volatilization, contaminating water supplies, communities, and ecosystems. Recent studies link exposure to childhood cancers and health impacts, while legal battles reveal regulatory gaps and economic pressures driving intensive chemical use.
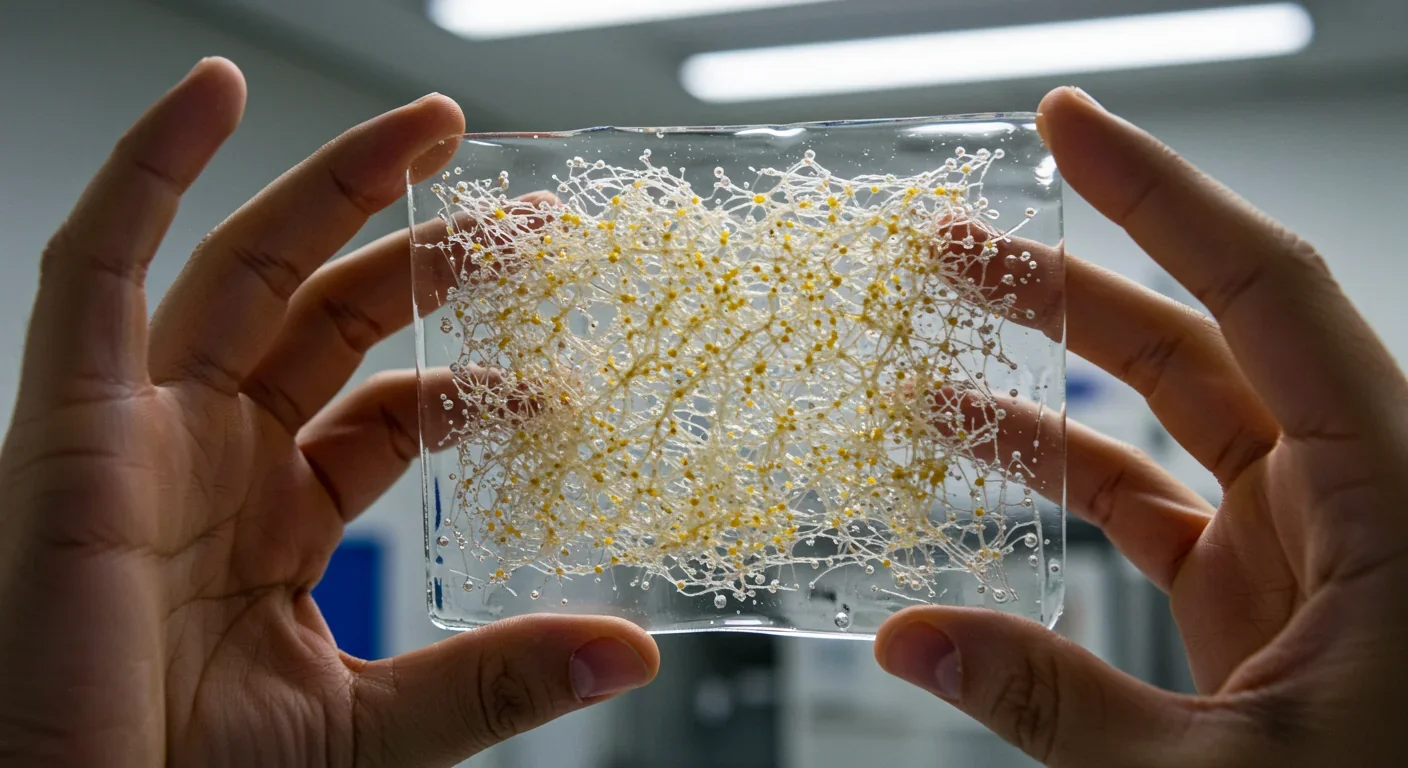

Scientists have discovered that tissue stiffening isn't just a symptom of aging and cancer - it's an active driver. The extracellular matrix hardens over time, mechanically instructing cells to malfunction, age faster, and become cancerous. This paradigm shift is spawning new therapies that target tissue mechanics rather than just cells, potentially revolutionizing treatment for age-related diseases and cancer.
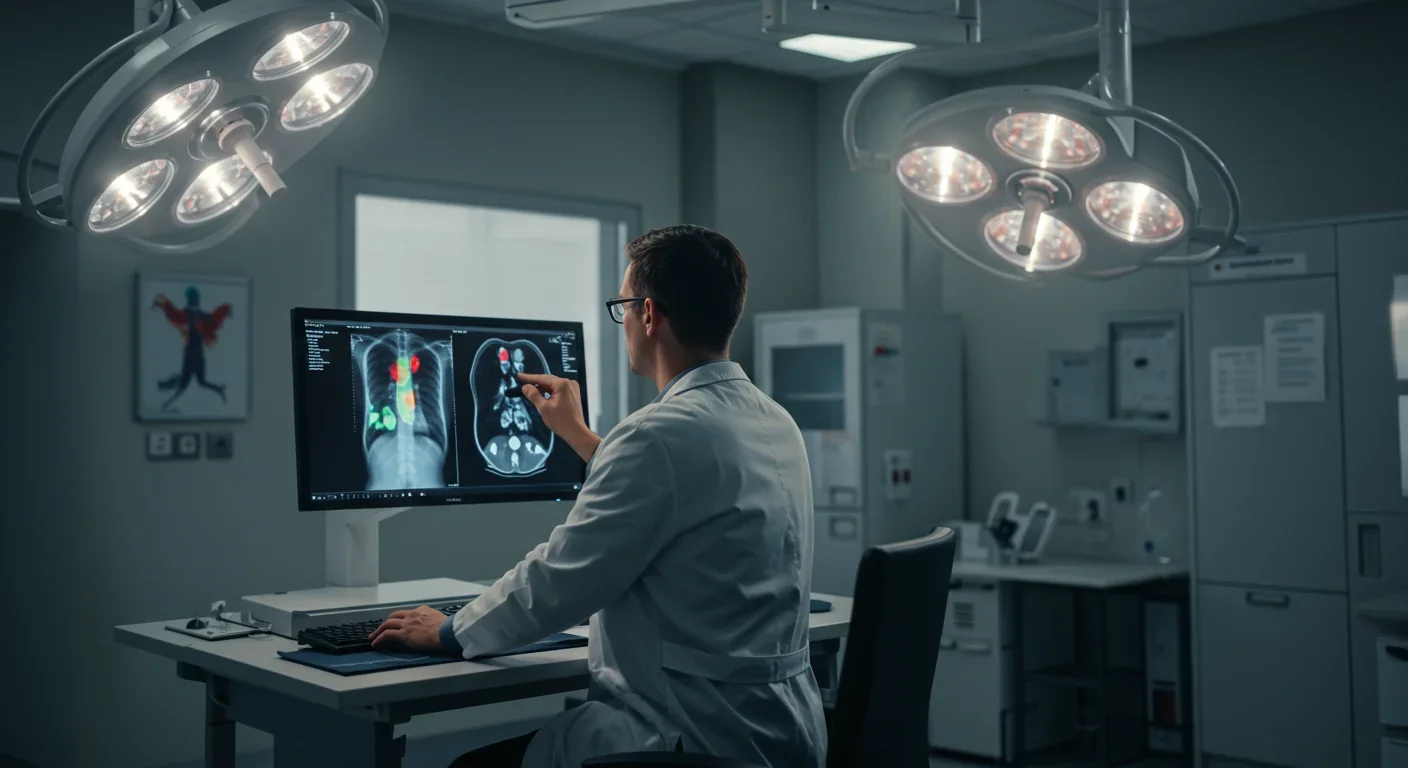
Explainable AI (XAI) is breaking down the black-box barrier in medical diagnostics, giving doctors visual explanations of how algorithms reach decisions through attention maps, SHAP scores, and counterfactual scenarios. While FDA regulations now mandate transparency in medical AI, real-world implementations show XAI improves both trust and diagnostic accuracy by transforming algorithms from mysterious oracles into collaborative partners that show their work.

Chemical cocktails can transform one cell type into another without altering DNA, offering a safer path to regenerative medicine than genetic methods. The first human trial showed success in treating diabetes, and applications span from neurological diseases to cardiac repair.
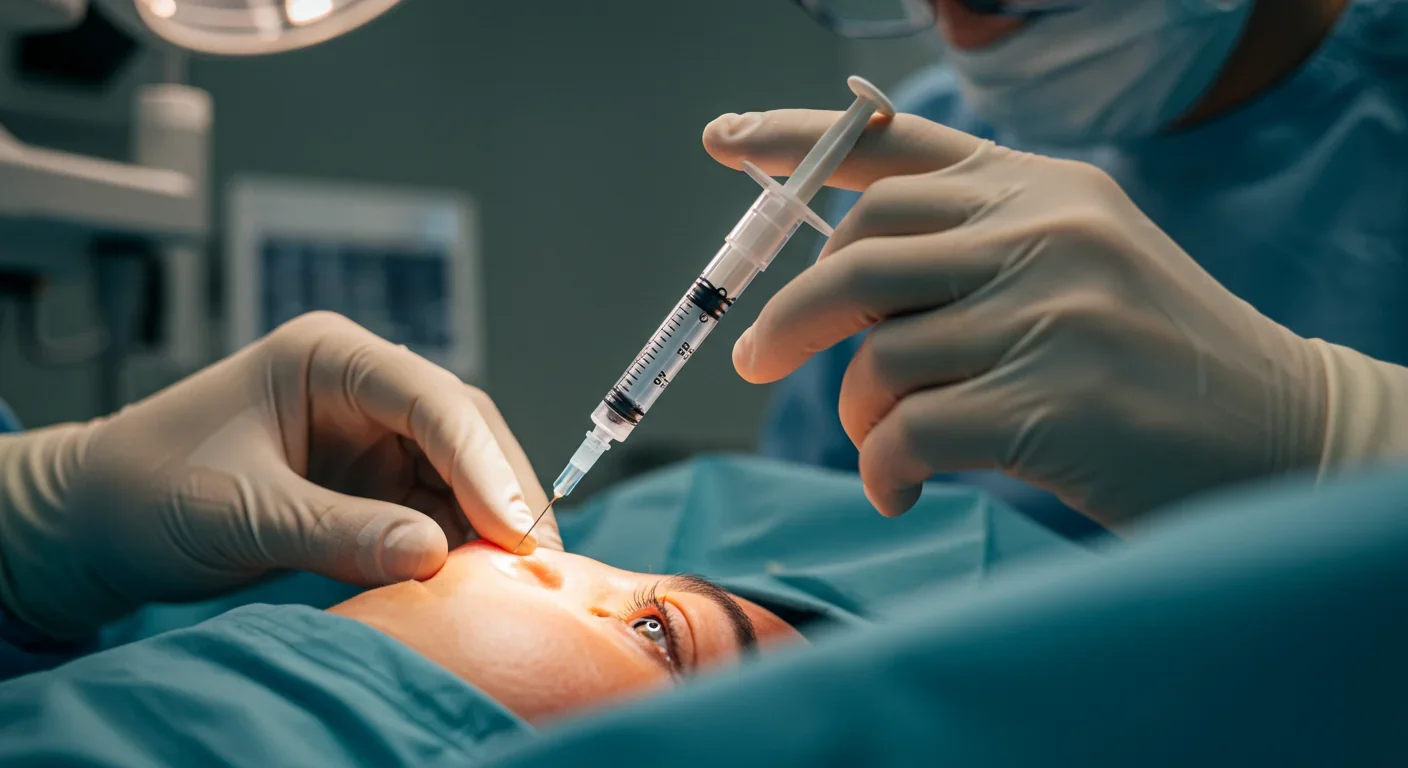
Optogenetic therapy is restoring vision to blind patients by engineering surviving retinal cells to become light-sensitive, bypassing dead photoreceptors. Recent clinical trials show patients with retinitis pigmentosa gaining functional vision after a single injection, enabling them to navigate spaces and locate objects for the first time in years.

Peroxisomes are cellular organelles that perform critical metabolic functions yet remain poorly understood. When they malfunction, they cause devastating diseases from severe infant conditions like Zellweger syndrome to adult disorders like adrenoleukodystrophy. New research is finally revealing their importance.
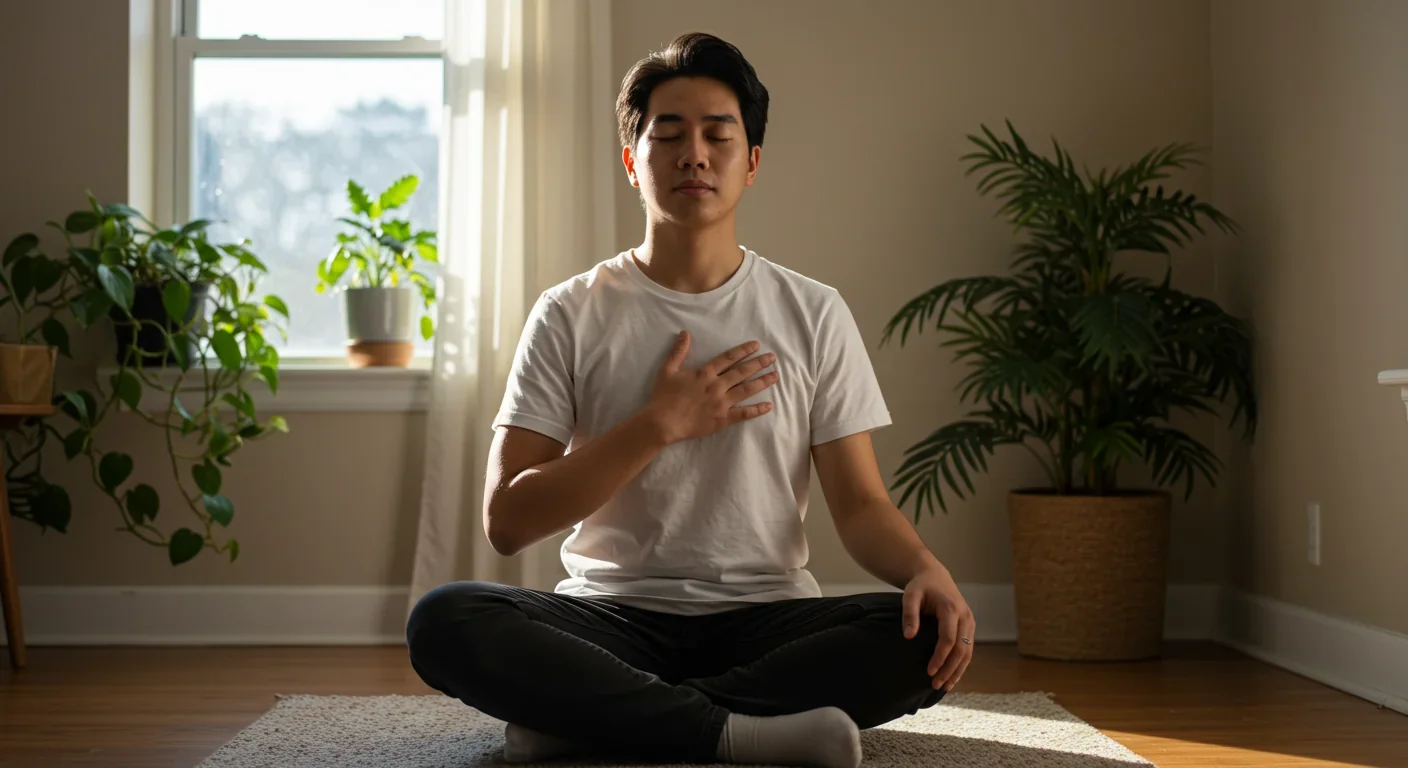

Your heartbeat pattern directly influences brain function, focus, and emotional control through measurable psychophysiological coherence. Simple breathing techniques can synchronize heart-brain communication to enhance cognitive performance and reduce stress within minutes.
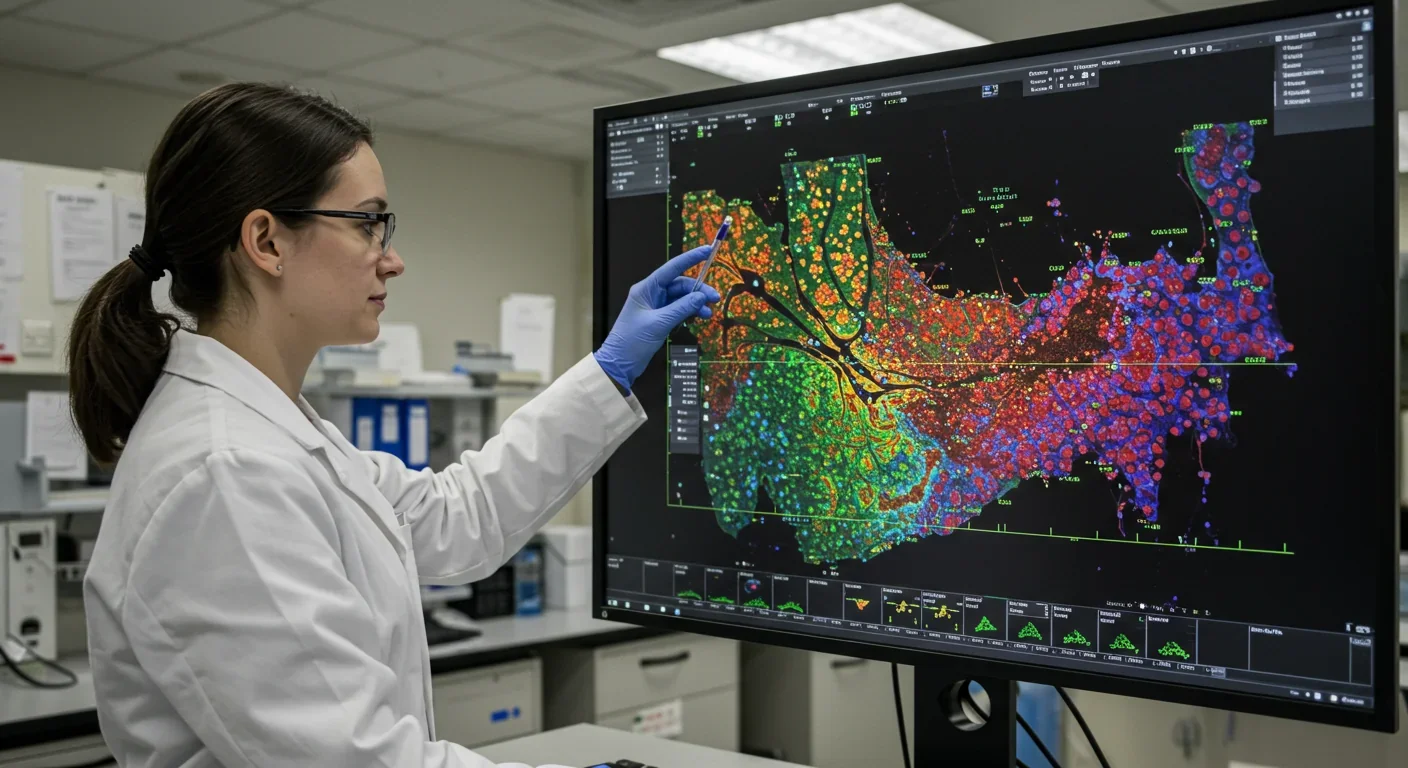
Spatial transcriptomics maps exactly where genes activate within tissues, transforming drug discovery by revealing how diseases organize spatially. The technology is accelerating pharmaceutical research, advancing precision medicine, and reshaping our understanding of cancer, neurological conditions, and human biology.
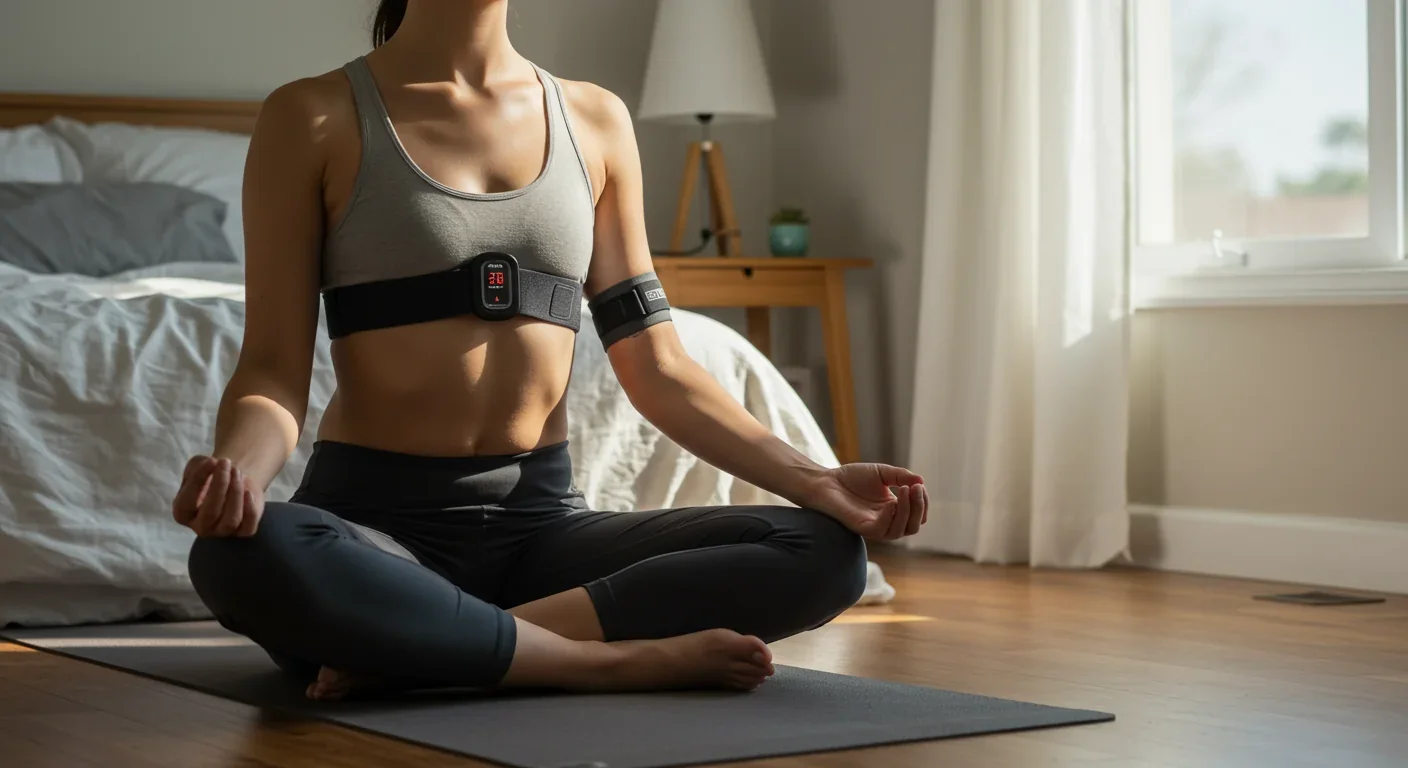

Heart rate variability training teaches you to optimize cardiac rhythm patterns through breathing exercises, reducing anxiety by rebalancing your autonomic nervous system - offering a scientifically-backed, non-pharmaceutical intervention that's now accessible through consumer wearables.

Hundreds of gut bacteria generate measurable electrical currents through extracellular electron transfer, potentially creating a bioelectric communication channel with the nervous system that operates alongside chemical gut-brain signaling.
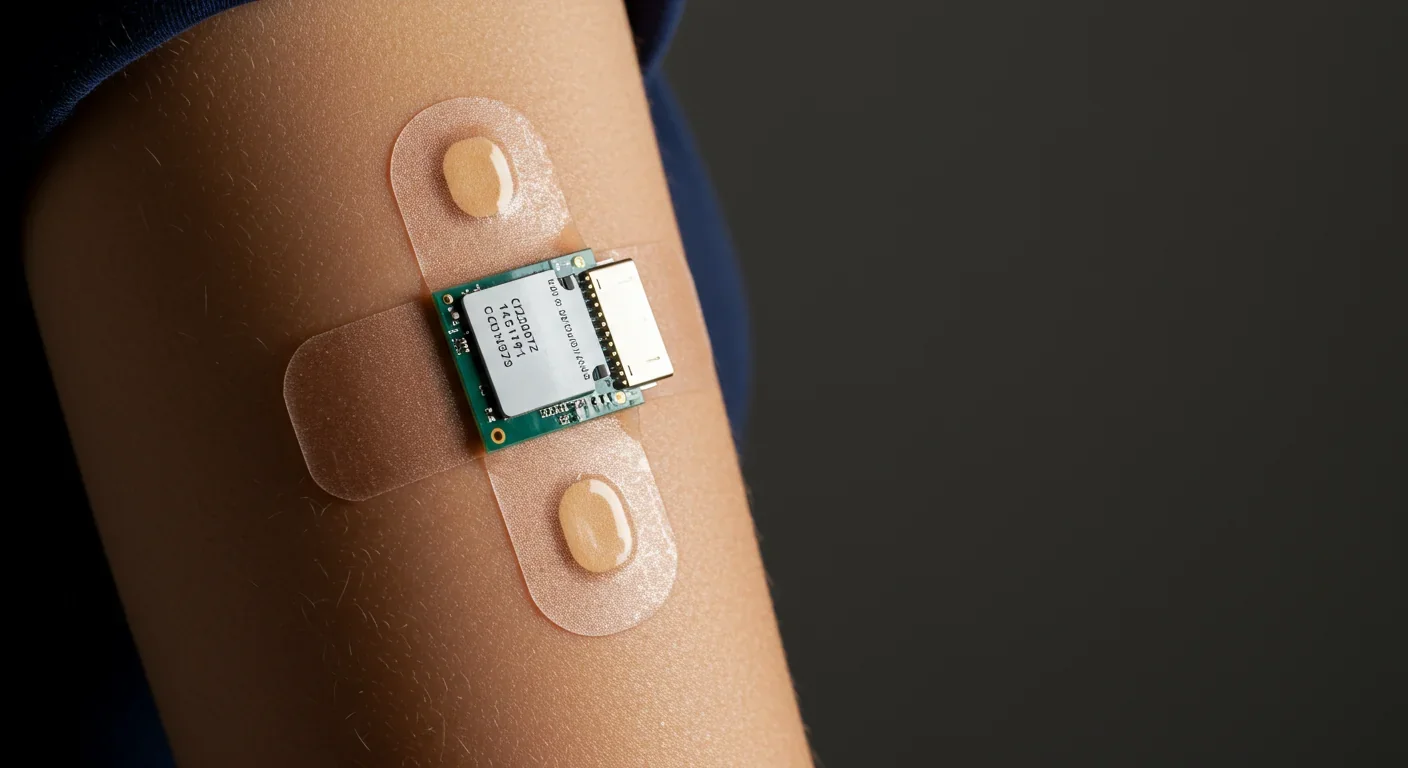
By 2030, wearable biosensors embedded in clothing could continuously monitor disease markers in your sweat, eliminating blood tests for many conditions. While devices are reaching FDA clearance today, accuracy challenges and privacy concerns remain as this technology transforms healthcare from episodic testing to continuous health surveillance.
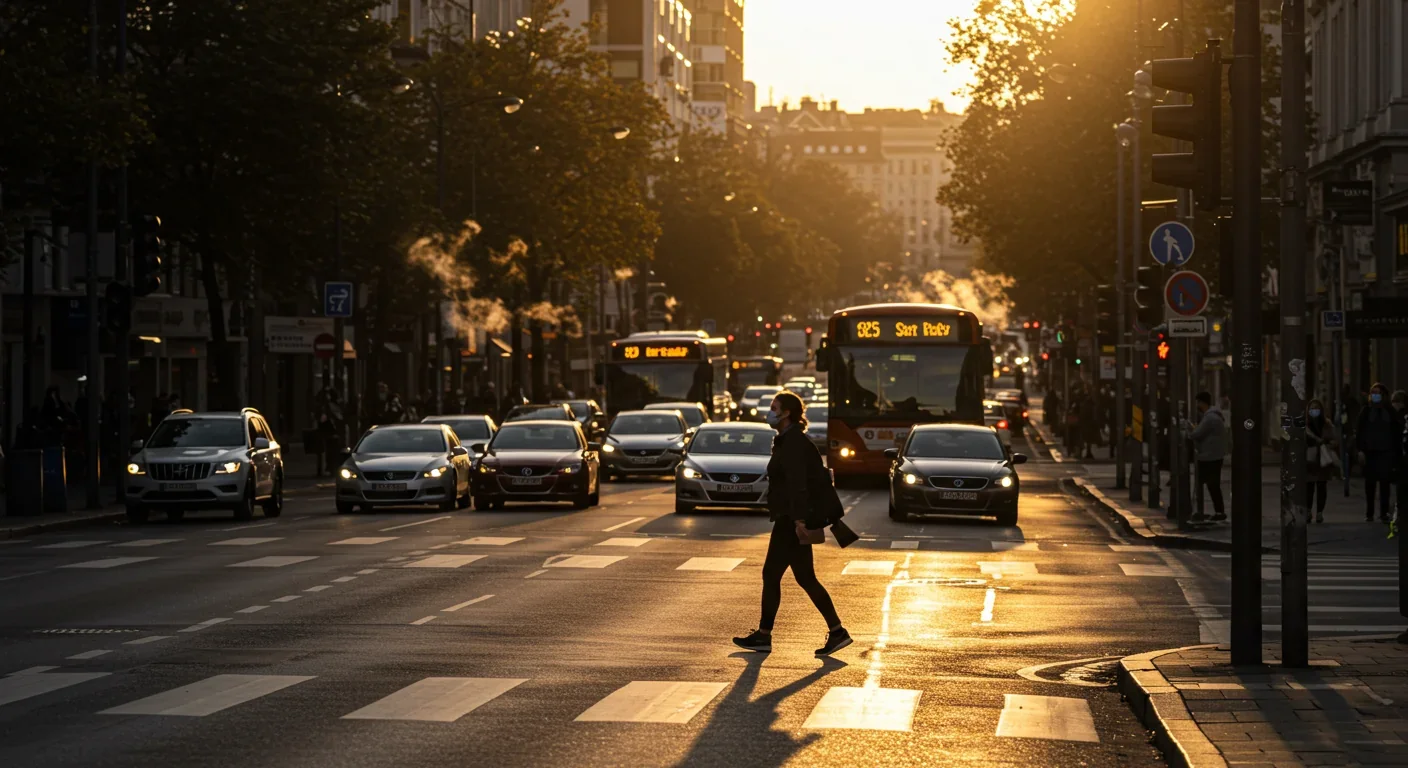

Ultrafine pollution particles smaller than 100 nanometers can bypass the blood-brain barrier through the olfactory nerve and bloodstream, depositing in brain tissue where they trigger neuroinflammation linked to dementia and neurological disorders, yet remain completely unregulated by current air quality standards.

RNA interference drugs silence disease-causing genes using tiny RNA molecules that destroy the messenger RNA before proteins are made. Seven FDA-approved RNAi drugs now treat previously untreatable genetic conditions, from ultra-rare disorders to cardiovascular disease.

Ancient microorganisms called archaea inhabit your gut and perform unique metabolic functions that bacteria cannot, including methane production that enhances nutrient extraction. These primordial partners may influence longevity and offer new therapeutic targets.

Proteostasis collapse - the breakdown of cellular protein quality control systems - connects Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, ALS, and other aging diseases through a common mechanism. New therapeutic strategies targeting chaperones, proteasomes, and autophagy offer hope for prevention and treatment.
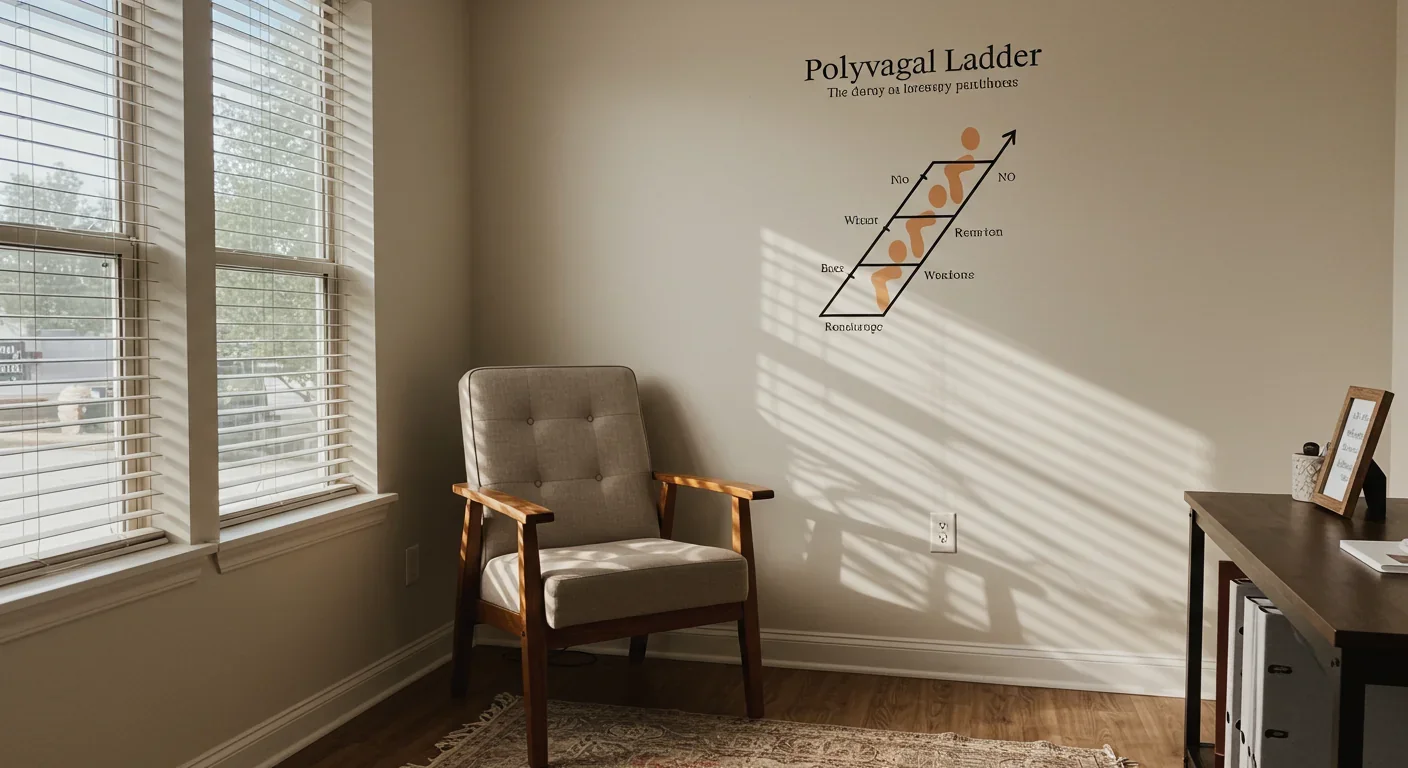

The polyvagal ladder translates neuroscience into a practical framework for treating trauma by mapping three nervous system states. Research shows promise for PTSD treatment, though evidence remains mixed and the approach has important limitations.

Controlled exposure to mild stressors triggers cellular defense mechanisms that extend lifespan - a biological phenomenon called hormesis that explains why practices from intermittent fasting to sauna use share the same longevity-promoting foundation.
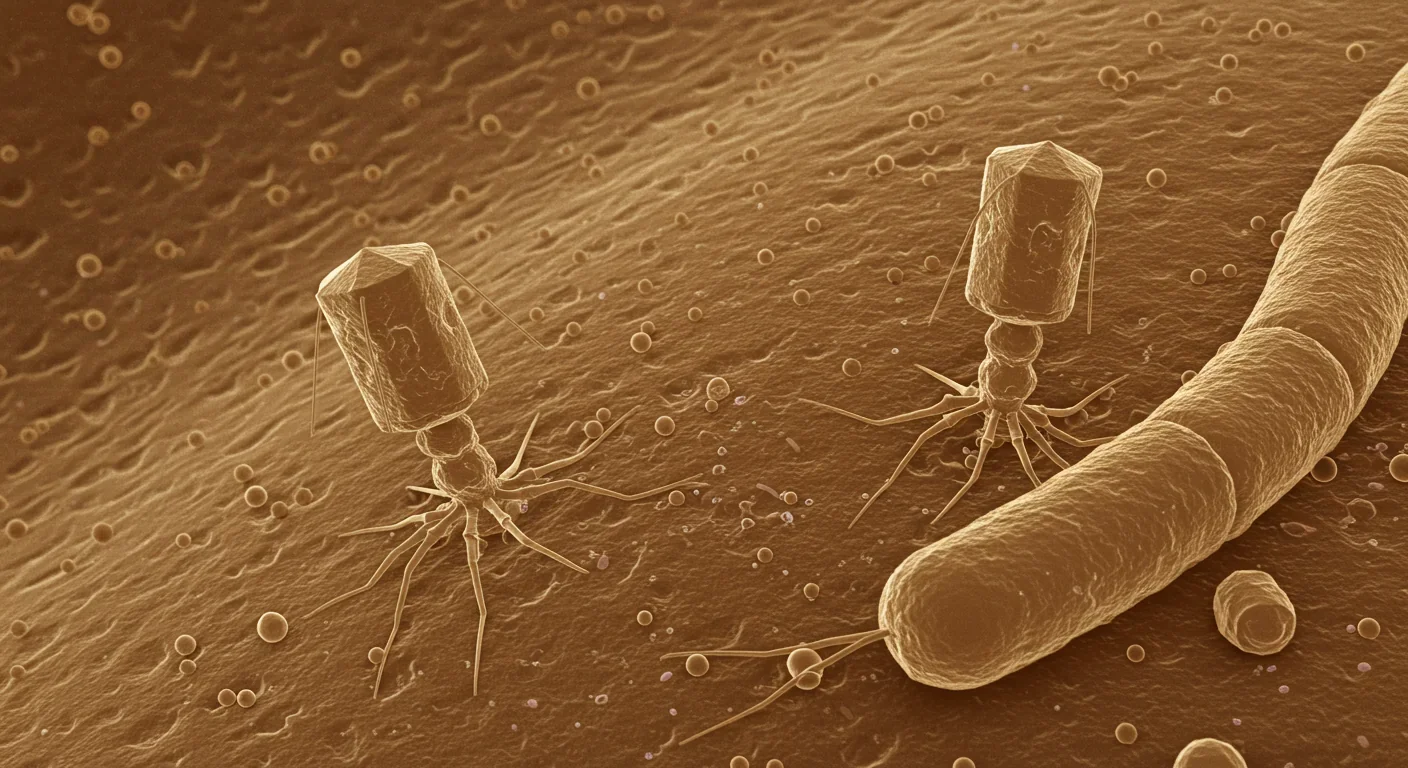
Your gut contains 10^15 viruses that wage constant warfare on bacteria, shaping your microbiome and health. New research reveals these bacteriophages are precision tools for treating antibiotic-resistant infections and chronic diseases.

Every day, billions of bacteria from your mouth travel to your gut, where specific pathogens can punch holes in your intestinal barrier and trigger inflammatory diseases affecting your heart, brain, joints, and more. The oral-gut bacterial highway represents a fundamental rethinking of how disease develops and spreads through the body.

Pharmacogenomic testing uses genetic information to predict how patients will respond to medications, potentially preventing thousands of adverse drug reactions annually. Major healthcare systems are implementing preemptive testing programs, though insurance coverage and equity challenges remain.

PFAS forever chemicals accumulate in human organs and blood with 97% of Americans showing detectable levels. These persistent compounds enter through water, food, and consumer products, with half-lives measured in years. New EPA regulations aim to protect 100 million people, but implementation delays mean continued exposure while remediation technologies advance.

Over 280 million pounds of glyphosate are applied annually in the U.S., with residues found in 60% of vegetables. Research shows 54% of core gut bacteria are vulnerable to this herbicide's antimicrobial effects, linking widespread exposure to rising metabolic diseases including fatty liver, diabetes, and obesity through microbiome disruption and leaky gut syndrome.

Telomere extension therapy could rejuvenate aging cells, but activating the enzyme telomerase risks triggering cancer. New approaches like ZSCAN4 gene therapy show promise in early trials, using alternative mechanisms to lengthen telomeres safely.

Up to 25% of Americans now experience chemical sensitivities triggered by everyday petrochemical exposure. Research reveals mast cell dysregulation and neurological changes as biological mechanisms behind Multiple Chemical Sensitivity, an emerging epidemic with serious public health implications.

CMA is a selective cellular cleanup system that targets damaged proteins for degradation. As we age, CMA declines - leading to toxic protein accumulation and neurodegeneration. Scientists are developing therapies to restore CMA function and potentially prevent brain diseases.

Loving-kindness meditation produces measurable brain changes in as little as eight weeks - increasing gray matter in empathy regions while reducing amygdala volume - and simultaneously lowers inflammatory markers like IL-6 and CRP by boosting vagal tone, making compassion practice a scientifically validated intervention with both neurological and immune system benefits.

Scientists have discovered that lipid rafts - tiny organized zones on cell membranes - control critical disease pathways in cancer, Alzheimer's, and infections. New therapies targeting these structures could revolutionize treatment.

Cross-link breakers are experimental drugs that could reverse arterial stiffening by breaking down AGE cross-links in blood vessel walls. Early compounds like alagebrium showed promise in animals but failed in humans because they didn't target glucosepane, the dominant cross-link in human tissue. New research funded by SENS Foundation is developing glucosepane-specific breakers that could genuinely reverse vascular aging.

Common gut bacterium Bacteroides fragilis produces a toxin (BFT) that damages intestinal barriers, triggers chronic inflammation, and promotes colorectal cancer in up to 88.5% of some patient populations. Scientists have identified a druggable target and potential prevention strategies.

Fecal virome transplants harness bacteriophages - viruses that hunt bacteria - to precision-engineer gut health, offering safer alternatives to traditional fecal transplants for treating inflammatory bowel disease, metabolic disorders, and immune conditions.

Base editing, a molecular pencil that rewrites single DNA letters without cutting strands, has just saved its first patients and promises to cure thousands of genetic diseases - but society isn't ready for the ethical questions it raises.

Scientific studies reveal electromagnetic hypersensitivity sufferers experience genuine symptoms but cannot detect EMF exposure better than chance, pointing to the nocebo effect rather than electromagnetic fields as the primary cause.

AI-powered genomic surveillance now tracks pathogen mutations in real time, predicting outbreaks before they spread - turning pandemic response from reactive chaos into proactive preparation.

Phthalates in everyday plastics reduce testosterone by up to 34% in boys and impair male fertility. These chemicals enter through food packaging and personal care products, affecting vulnerable populations disproportionately.

Naked mole rats survive 18 minutes without oxygen by switching to fructose metabolism, a plant-like pathway that could revolutionize treatment for strokes, cardiac arrest, and organ preservation in humans.
Scientists are revolutionizing gut health by identifying 'keystone' bacteria - crucial microbes that hold entire microbial ecosystems together. By engineering and reintroducing these missing bacterial linchpins, researchers can transform dysfunctional microbiomes into healthy ones, opening new treatments for diseases from IBS to depression.
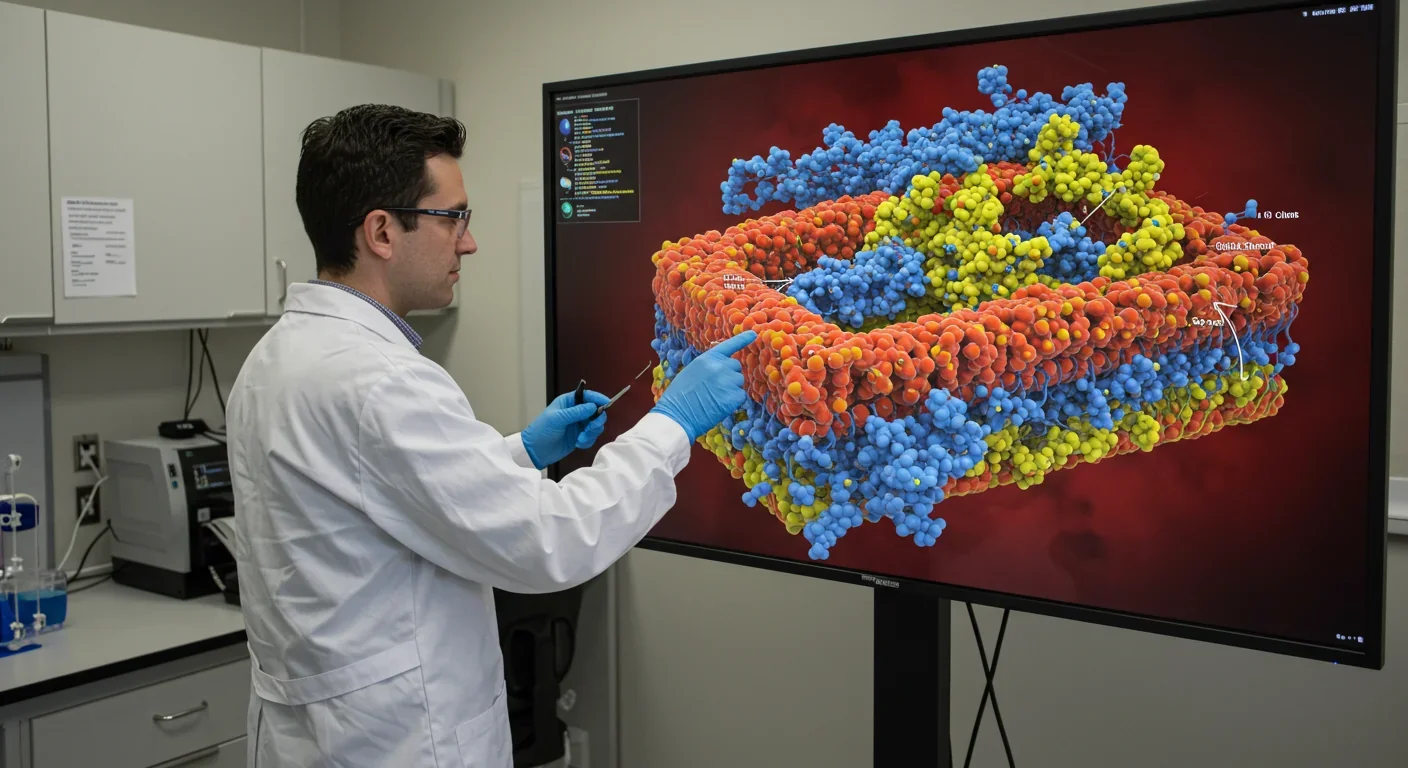
Lipid rafts are cholesterol-rich membrane platforms that organize cell signaling. Their disruption drives diseases from Alzheimer's to cancer, and restoring raft integrity represents a promising new therapeutic frontier.

Wildfire smoke triggers autoimmune flares through PM2.5 particles that activate immune danger sensors, inflammasomes, and B-cell hyperactivity. A landmark study of 80,000 veterans confirmed the link between wildfire exposure and rheumatoid arthritis flares.
Scientists are building AI-powered genomic weather forecast systems that track pathogen mutations in real-time to predict disease outbreaks before they happen, transforming pandemic response from reactive to proactive.

Photobiomodulation (PBM) uses specific wavelengths of red and near-infrared light (630 - 900 nm) to penetrate skin and stimulate mitochondria, boosting cellular energy production by up to 30%. Clinical studies show PBM improves skin rejuvenation, accelerates athletic recovery, reduces chronic pain, and may enhance mood and sleep - all without drugs or surgery. However, consumers must navigate dosing complexities, regulatory gaps, and device quality issues. With over 5,000 peer-reviewed studies an...

Scientists are pursuing therapies to reverse glycation, the process where sugar molecules permanently bond with proteins, causing tissue stiffness and aging. While early drugs failed, new approaches targeting specific cross-links and prevention strategies offer hope.

Ten minutes in nature measurably lowers cortisol, reduces heart rate, and shifts your nervous system toward rest. The biophilia effect isn't mystical - it's quantifiable physiology, and doctors are now prescribing park time alongside medication.
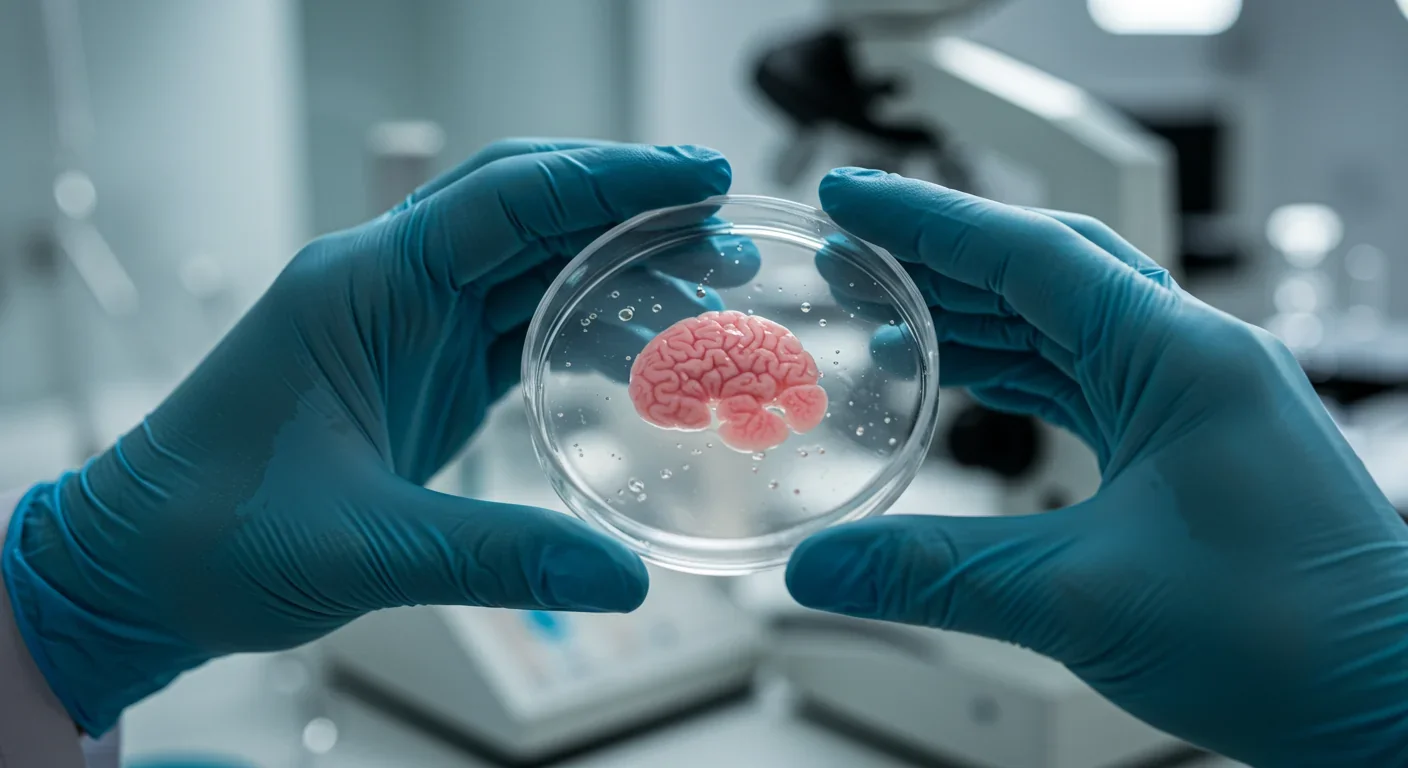

Lab-grown miniature human brains called organoids are replacing animal testing in drug development, achieving 85-90% accuracy in predicting human drug responses compared to animals' 50-60% rate, while the FDA phases out animal trials in favor of this faster, more ethical approach.

Mycotoxins from hidden indoor mold are causing chronic illnesses in millions. Research now confirms these invisible toxins trigger neurological damage, immune suppression, and systemic inflammation, with testing and treatment protocols available for those suffering from unexplained symptoms.

Ferroptosis, a form of iron-dependent cell death, is emerging as a revolutionary cancer treatment that exploits tumors' iron addiction. Unlike conventional therapies, it bypasses resistance mechanisms and may transform how we fight treatment-resistant cancers by 2030.

Epigenetic clocks measure biological age through DNA methylation patterns and can predict chronic disease risk 20-30 years before symptoms emerge, offering unprecedented opportunities for prevention while raising profound questions about privacy, equity, and what we do when we can see our biological future.
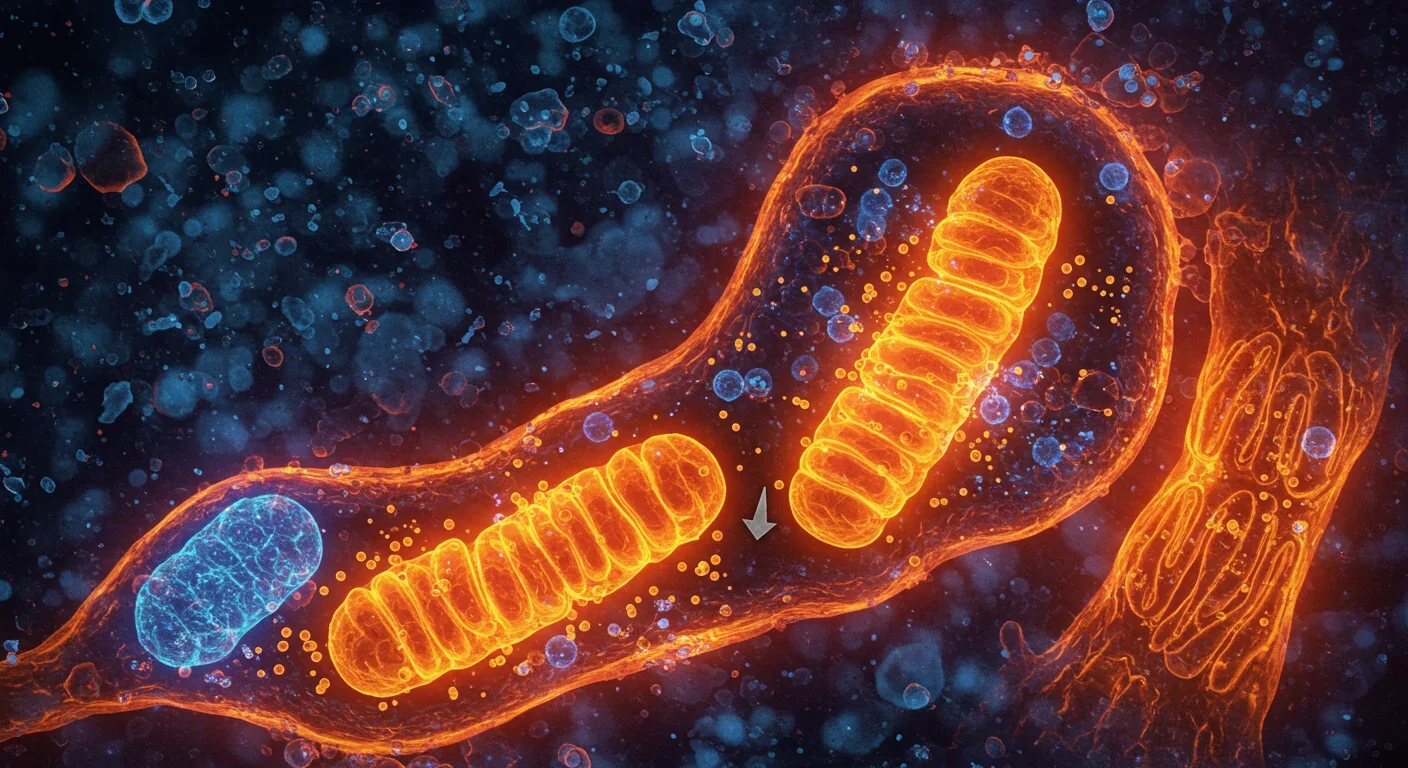
Mitophagy - your cells' cleanup mechanism for damaged mitochondria - holds the key to preventing Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, heart disease, and diabetes. Scientists have discovered you can boost this process through exercise, fasting, and specific compounds like spermidine and urolithin A.

Learning to sense your body's internal signals through interoception training can reduce anxiety and chronic pain without medication, backed by neuroscience research showing measurable brain changes.
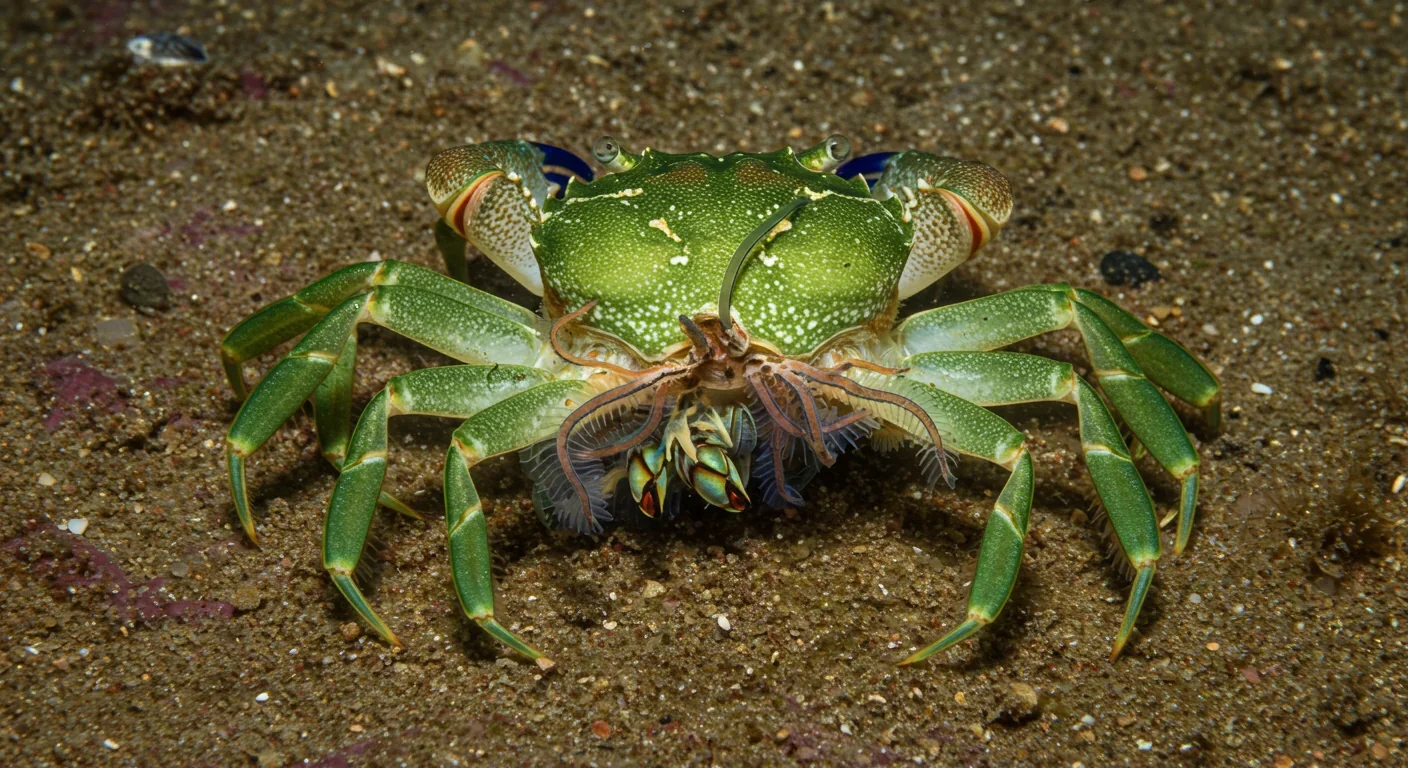

Parasites have evolved sophisticated strategies to hijack host reproduction, from barnacles that chemically castrate crabs to wasps that inject mind-controlling viruses. These mechanisms reshape ecosystems, drive evolution, and offer both risks and opportunities for pest control and disease management.
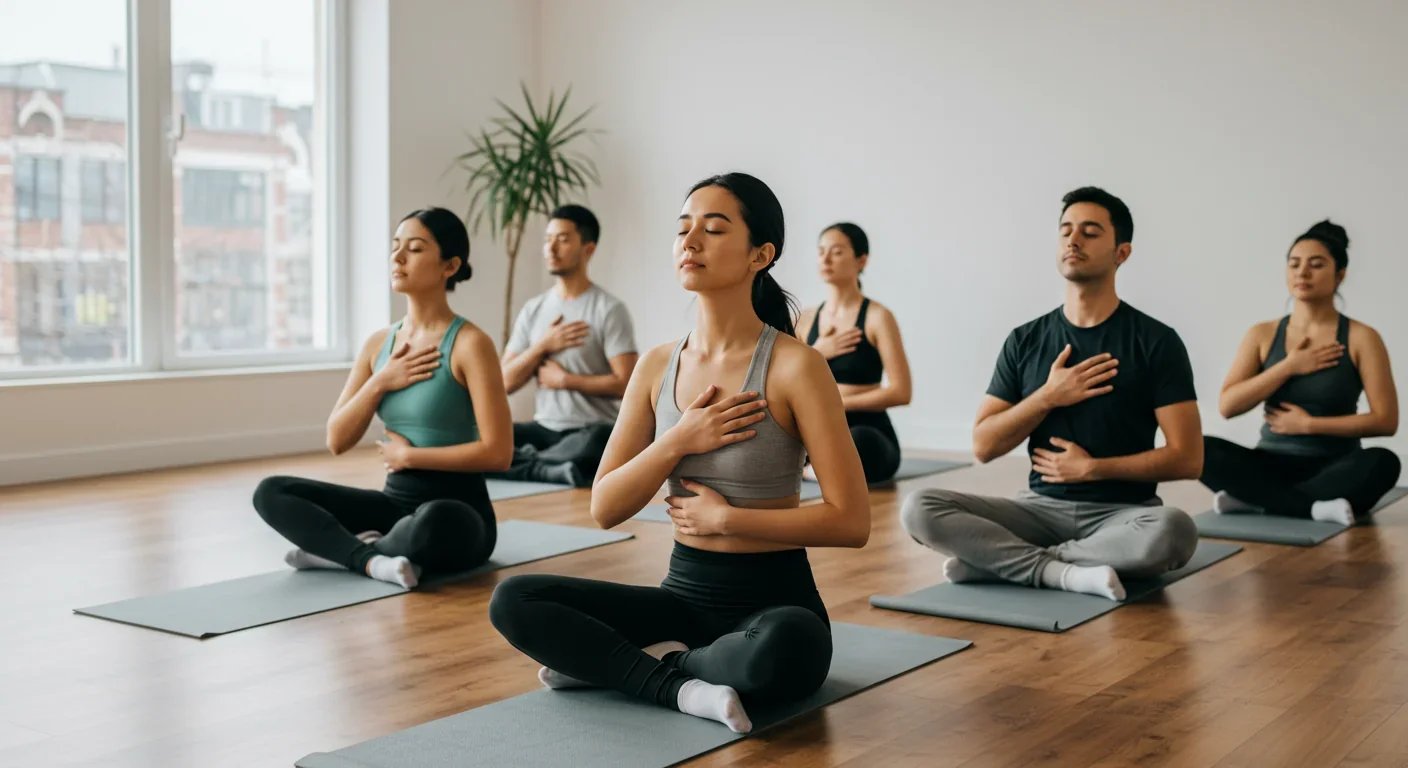

Interoception - your body's ability to sense internal signals like heartbeat and breathing - shapes every emotion you feel and your sense of self. By training this hidden sense through practices like heartbeat detection and body scans, you can enhance emotional awareness and mental wellbeing.

Base editing fixes genetic mutations by chemically converting single DNA letters without cutting DNA strands, making it safer than traditional CRISPR. Already curing sickle cell disease and inherited blindness, this breakthrough technology could transform medicine while raising urgent questions about access, ethics, and the future of human genetics.

Social media has created a trauma economy where personal suffering is monetized through platforms like TikTok, Patreon, and GoFundMe, raising ethical questions about exploitation, mental health impacts, and the commodification of pain.
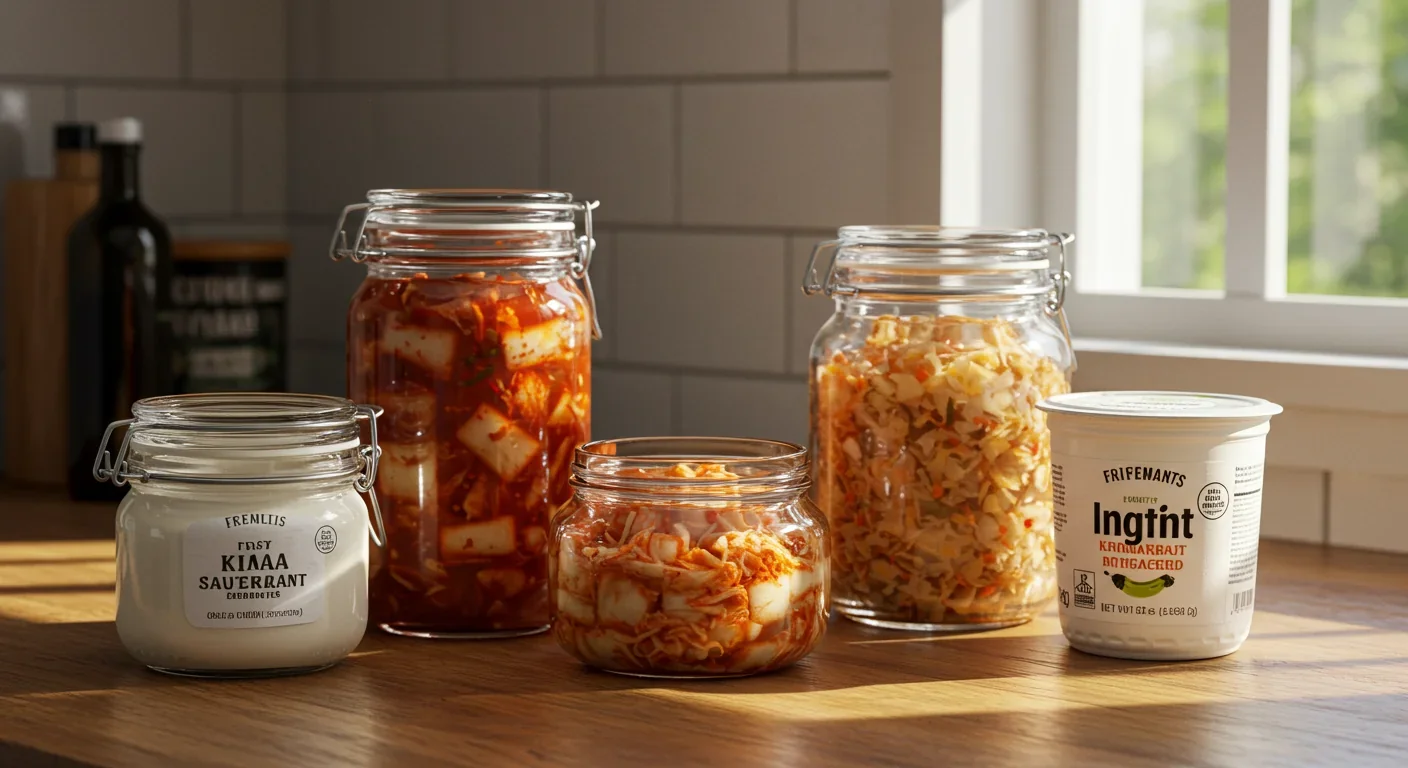

Postbiotics are non-living bacterial byproducts that may offer gut health benefits without the challenges of keeping probiotics alive, potentially transforming how we approach microbiome wellness.

CAR-T cell therapy, originally developed for cancer, is showing remarkable success in treating autoimmune diseases by eliminating rogue B cells and allowing the immune system to reset, with early trials achieving drug-free remissions in lupus, MS, and other conditions.
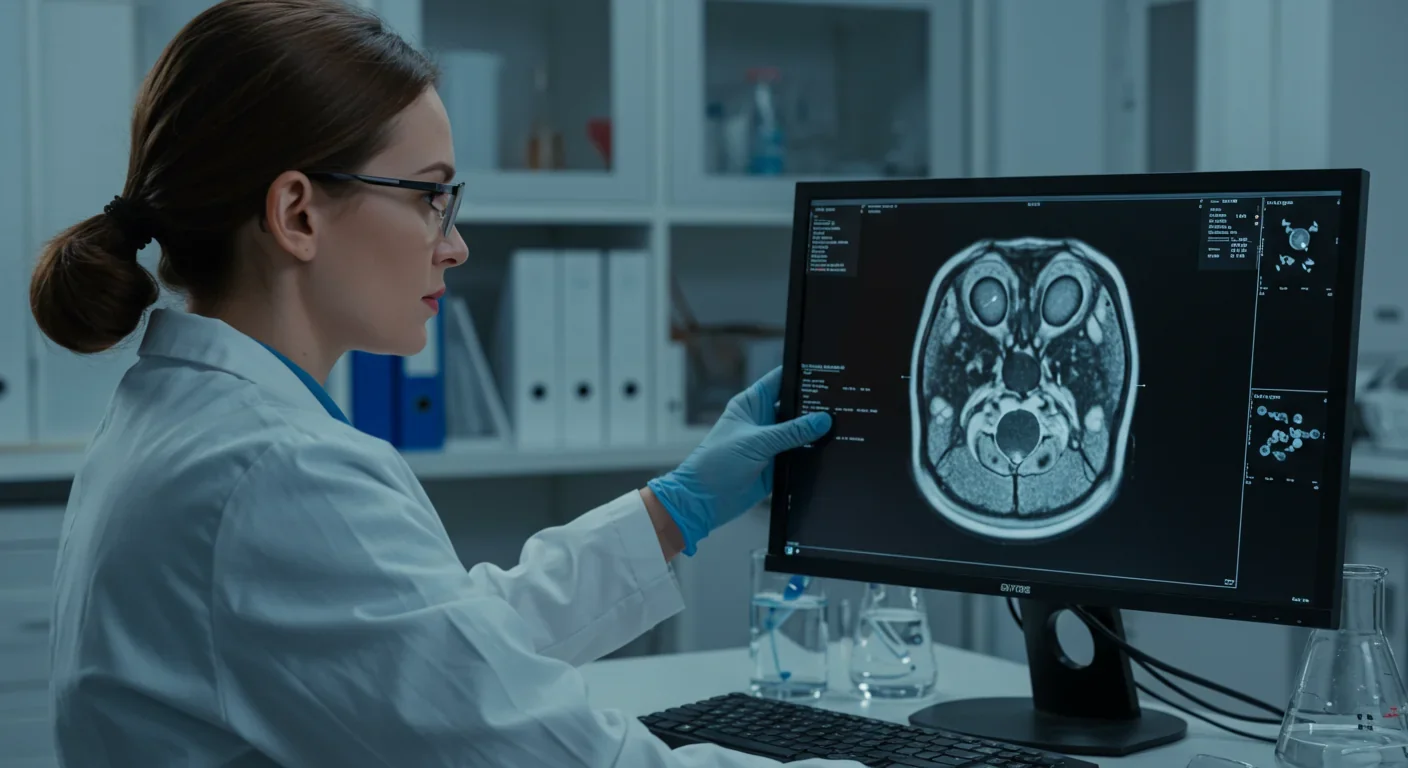

Scientists are reversing immune aging by regenerating the thymus - a critical organ that trains T-cells but shrinks with age. Clinical trials show hormone therapies can restore thymic function and even reverse biological age markers, with treatments potentially available within a decade.

Multiomics integration combines genome, proteome, and metabolome analysis to predict diseases years before symptoms appear, revolutionizing preventive medicine with unprecedented accuracy for conditions like cancer and Alzheimer's.

Horseshoe crabs, living fossils that survived 450 million years, have blue blood containing cells that detect bacterial contamination. This makes their blood essential for testing every vaccine and injectable drug, but synthetic alternatives now offer a sustainable path forward.

Scientists are engineering keystone bacterial species like F. prausnitzii and A. muciniphila to restore gut health and treat diseases from IBD to cancer, using tools like CRISPR and synthetic biology to create precision therapies.

Blood protein profiling can now predict disease risk years before symptoms appear by analyzing thousands of proteins simultaneously, enabling personalized prevention and early intervention - but raises urgent questions about access, privacy, and healthcare equity.

The global longevity economy, driven by aging populations and projected to reach $63 billion by 2035, represents the largest wealth transfer in history. Businesses that understand this demographic shift and build for dignity, independence, and long-term value will capture trillions in opportunities across healthcare, finance, housing, technology, and leisure sectors.

Adult brains can change through neuroplasticity, but within strict biological limits. Evidence supports exercise, skill learning, and environmental enrichment, while debunking claims of limitless transformation. Age brings constraints, not possibilities for reversal.

Rainforests hold undiscovered medicines that could revolutionize healthcare, but deforestation threatens species extinction before their therapeutic potential is realized. Success requires balancing pharmaceutical innovation with conservation, indigenous rights, and equitable benefit-sharing under evolving legal frameworks.

Stem cell therapies are moving from laboratory promise to clinical reality, with patients walking after paralysis and damaged organs regenerating. Yet regulatory caution, manufacturing challenges, and inconsistent results mean the revolution will arrive gradually, transforming not just medicine but how humanity thinks about aging and human limitation.

Gut bacteria are revolutionizing medicine as scientists develop microbiome-based therapies to treat diseases from infections to autoimmune disorders, with FDA-approved treatments already available and personalized microbial medicine on the horizon.

Higher BMI may surprisingly protect against death in critical illness, challenging decades of weight-loss advice. Research reveals complex biological mechanisms where metabolic reserves, mental health, and fitness matter more than the scale.

Human enhancement technologies like CRISPR, brain implants, and AI are advancing rapidly, forcing society to confront ethical questions about equity, consent, and what it means to be human before irreversible changes reshape our species.

Senescent zombie cells refuse to die and secrete inflammatory factors that accelerate aging and chronic diseases. New therapies called senolytics can eliminate these cells, potentially extending healthy lifespan and preventing conditions from arthritis to neurodegeneration.
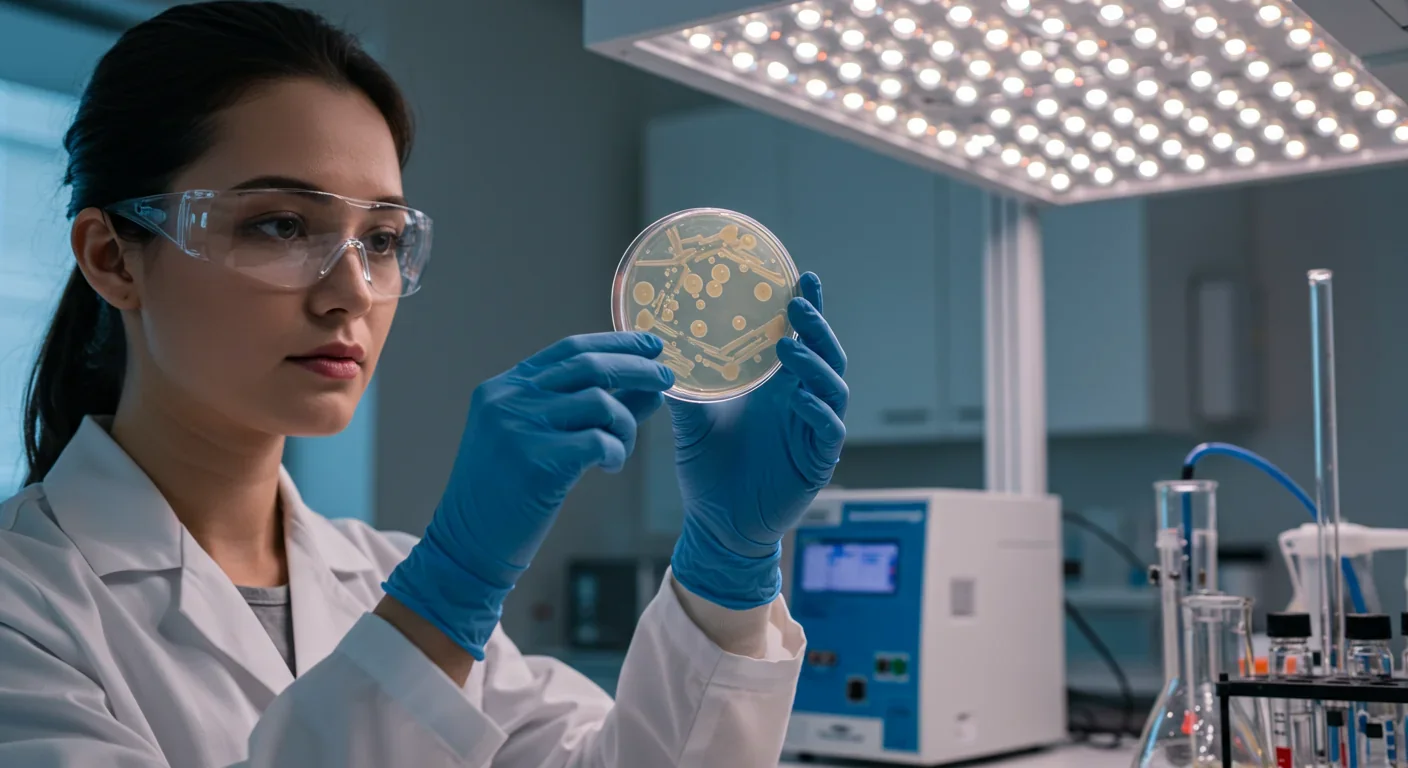

A gut bacterium called Akkermansia muciniphila shows promise against metabolic syndrome by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation. You can boost it through polyphenol-rich foods, fiber, and intermittent fasting, or try new heat-killed probiotic supplements.
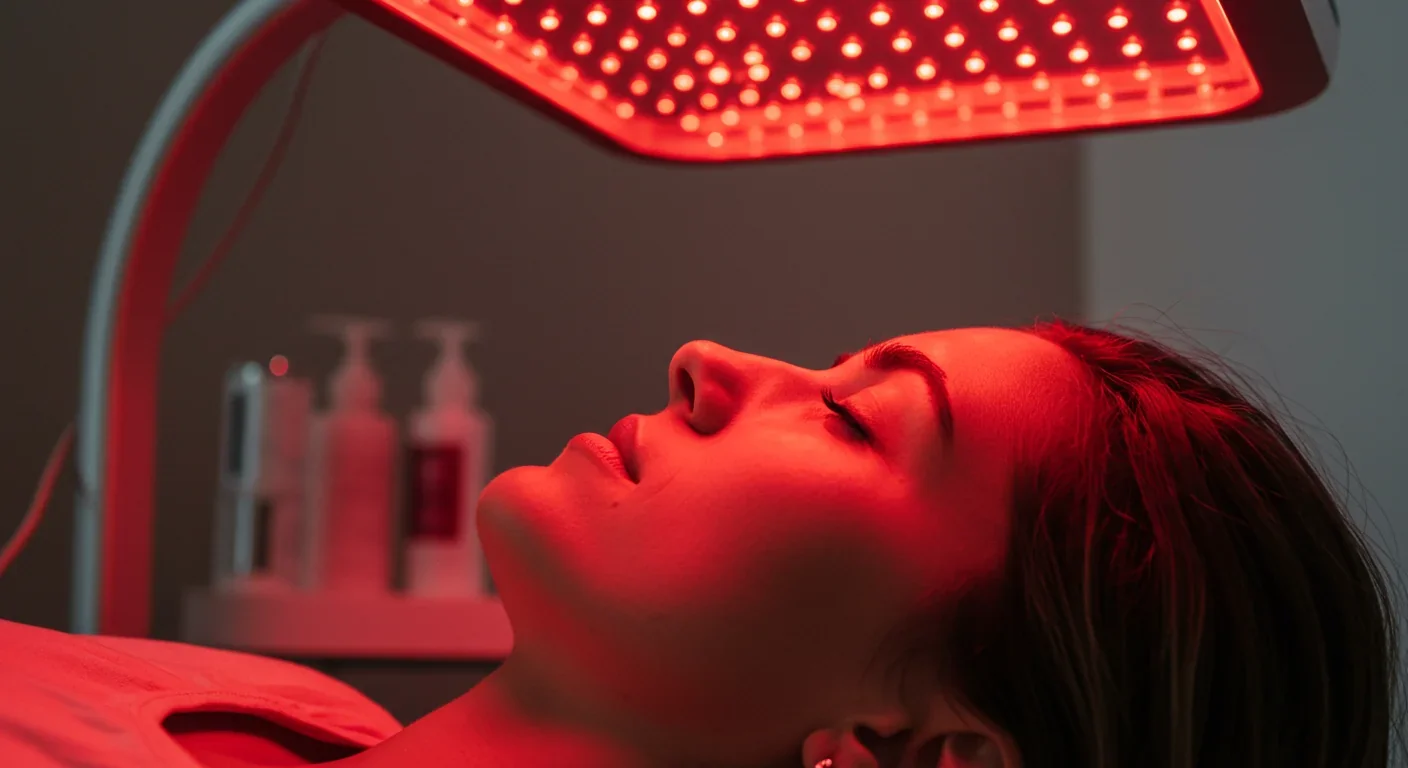

Red and near-infrared light can penetrate your cells and recharge mitochondria, triggering healing responses that reduce inflammation, repair tissue, and boost energy. Photobiomodulation is backed by clinical evidence for pain relief, wound healing, and vision protection, though choosing the right device and dosage is crucial for results.
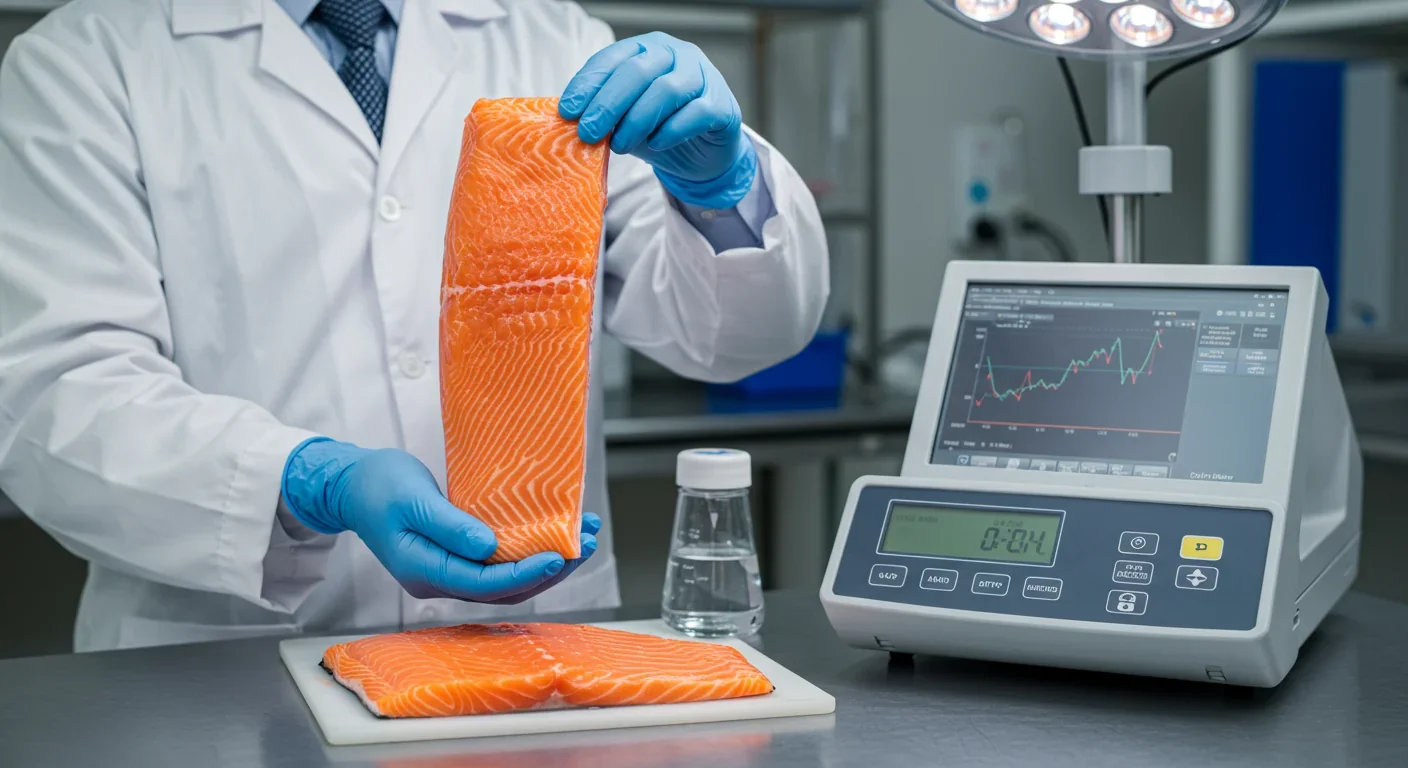

Toxins like mercury and PCBs concentrate as they move up the food chain through biomagnification, turning trace contaminants into health risks. Understanding which fish to eat, how often, and supporting cleaner ecosystems helps protect your health.

Neuroscience has mapped the exact brain circuits that govern love and attachment - the amygdala for threat detection, the ventral striatum for reward, and the prefrontal cortex for regulation. Researchers can now predict your attachment style from one second of brain activity with over 90% accuracy, opening doors to objective assessments and targeted therapies that could break intergenerational cycles of relationship dysfunction. By 2030, brain-based interventions may reshape how we form bonds,...

Medical AI systems are amplifying racial and economic disparities in healthcare through biased training data, proxy variables, and opaque algorithms. Solutions include transfer learning, diverse datasets, and continuous monitoring.
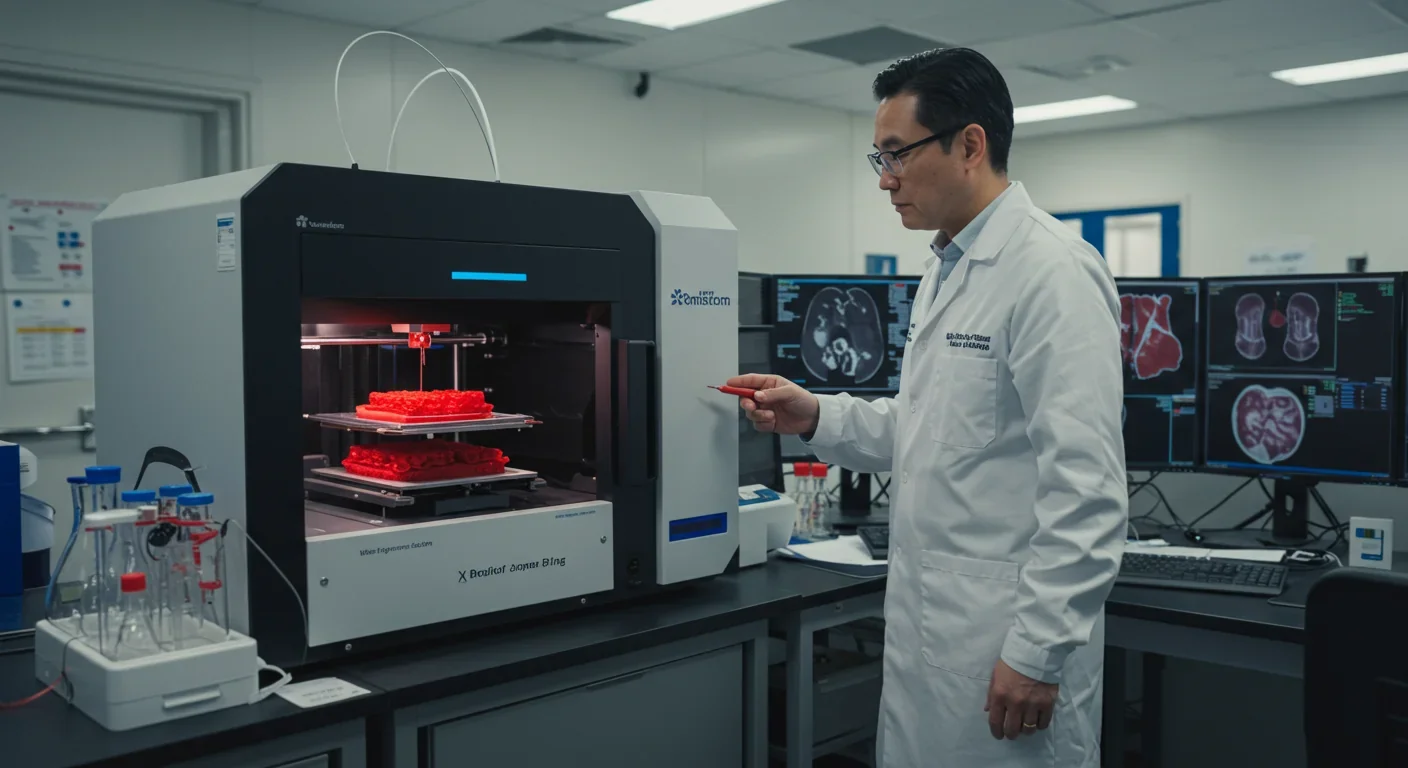

Artificial organs grown from 3D-printed tissue and lab cultures are moving from science fiction to clinical reality, potentially eliminating transplant waiting lists within decades. But breakthroughs in vascularization and bioprinting bring profound challenges around access, ethics, and regulation.

Scientists are pioneering mitochondrial transplants that replace damaged cellular powerhouses with healthy ones, showing promise for treating Parkinson's, heart failure, stroke, and aging itself - with first clinical trials launching now.

Your expectations can literally change your brain chemistry. The placebo effect triggers real biochemical responses through neural networks, producing measurable improvements in chronic pain, depression, and other conditions - even when patients know they're receiving inactive treatments.
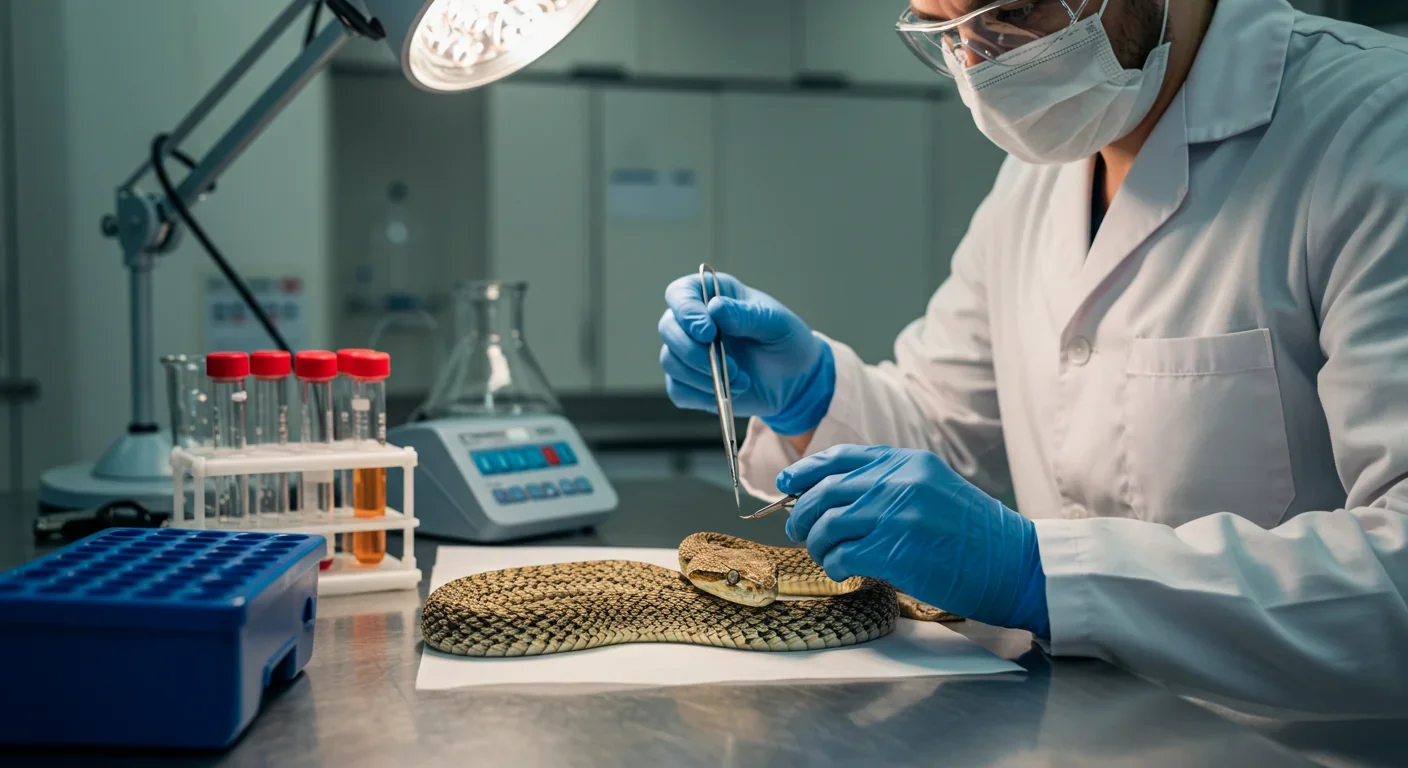

Scientists are transforming deadly venoms from snakes, spiders, and marine creatures into life-saving medicines. From captopril for blood pressure to exenatide for diabetes, venom-derived drugs showcase how nature's chemical arsenal can be repurposed for healing.